Room-Temperature Magnetism of Ceria Nanocubes by Inductively Transferring Electrons to Ce Atoms from Nearby Oxygen Vacancy
Corresponding Author: Chenguo Hu
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 8 No. 1 (2016), Article Number: 13-19
Abstract
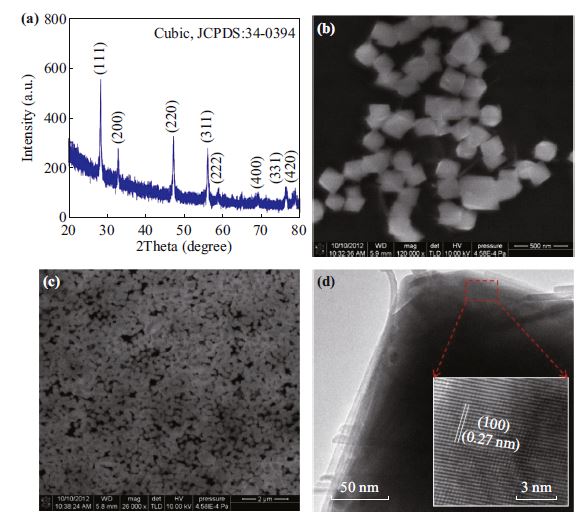
Ceria (CeO2) nanocubes were synthesized by a hydrothermal method and weak ferromagnetism was observed in room temperature. After ultraviolet irradiation, the saturation magnetization was significantly enhanced from ~3.18 × 10−3 to ~1.89 × 10−2 emu g−1. This is due to the increase of oxygen vacancies in CeO2 structure which was confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectra. The first-principle calculation with Vienna ab-initio simulation package was used to illustrate the enhanced ferromagnetism mechanism after calculating the density of states (DOSs) and partial density of states (PDOSs) of CeO2 without and with different oxygen vacancies. It was found that the increase of oxygen vacancies will enlarge the PDOSs of Ce 4f orbital and DOSs. Two electrons in one oxygen vacancy are respectively excited to 4f orbital of two Ce atoms neighboring the vacancy, making these electron spin directions on 4f orbitals of these two Ce atoms parallel. This superexchange interaction leads to the formation of ferromagnetism in CeO2 at room temperature. Our work indicates that ultraviolet irradiation is an effective method to enhance the magnetism of CeO2 nanocube, and the first-principle calculation can understand well the enhanced magnetism.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- X.L. Wang, S.Z. Yi, E.W. Liang, Y.Y. Wu, Z.X. Fang, Study on preparation of polishing powder for LCD. Adv. Mater. Res. 785–786, 480–483 (2013). doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.785-786.480
- Y. Chen, Z.N. Li, N.M. Miao, Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)/CeO2 hybrid particles for enhanced chemical mechanical polishing performance. Tribol. Int. 82, 211–217 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2014.10.013
- M. Ozawa, Role of cerium-zirconium mixed oxides as catalysts for car pollution: a short review. J. Alloy. Compd. 275, 886–890 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(98)00477-0
- S.Y. Christou, S. Garacia-Rodriguez, J.L.G. Fierro, A.M. Efstathiou, Deactivation of Pd/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 model three-way catalyst by P, Ca and Zn deposition. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 111, 233–245 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.10.004
- Z.X. Yang, X.H. Yu, Z.S. Lu, S.F. Li, K. Hermansson, Oxygen vacancy pairs on CeO2 (110): a DFT+U study. Phys. Lett. A 373(31), 2786–2792 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2009.05.055
- K.C. Anjaneya, G.P. Nayaka, J. Manjanna, G. Govindaraj, K.N. Ganesha, Preparation and characterization of Ce1-xGdxO2-delta (x = 0.1–0.3) as solid electrolyte for intermediate temperature SOFC. J. Alloy. Compd. 578, 53–59 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.05.010
- E. Bekyarova, P. Fornasiero, J. Kaspar, M. Graziani, CO oxidation on Pd/CeO2-ZrO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 45(1–4), 179–183 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00212-0
- H. Yahiro, Y. Baba, K. Eguchi, H. Arai, High-temperature fuel-cell with ceria-yttria solid electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135(8), 2077–2080 (1988). doi:10.1149/1.2096212
- M.F. Al-Kuhaili, S.M.A. Durrani, I.A. Bakhtiari, Carbon monoxide gas-sensing of CeO2-ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(5), 3033–3039 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.08.058
- B. Choudhury, A. Choudhury, Ce3+ and oxygen vacancy mediated tuning of structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 131(3), 666–671 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.10.032
- Y. Taga, Recent progress in coating technology for surface modification of automotive glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 218, 335–341 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(97)00281-0
- S. Zec, S. Boskovic, B. Kaluderovic, Z. Bogdanov, N. Popovic, Chemical reduction of nanocrystalline CeO2. Ceram. Int. 35(1), 195–198 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.10.031
- L. Zhang, H. Jiang, M. Selke, X.M. Wang, Selective cytotoxicity effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles under UV irradiation. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 10(2), 278–286 (2014). doi:10.1166/jbn.2014.1790
- R. Si, M. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 47(15), 2884–2887 (2008). doi:10.1002/anie.200705828
- N. Izu, S. Nishizaki, T. Itoh, M. Nishibori, W. Shin, I. Matsubara, Gas response, response time and selectivity of a resistive CO sensor based on two connected CeO2 thick films with various particles sizes. Sens. Actuators B 136(2), 364–370 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.snb.2008.12.018
- M. Nolan, Hybrid density functional theory description of oxygen vacancies in the CeO2 (110) and (100). Chem. Phys. Lett. 499(1–3), 126–130 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2010.09.016
- X.P. Han, J.C. Lee, H.I. Yoo, Oxygen-vacancy-induced ferromagnetism in CeO2 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 79(10), 100403 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.79.100403
- S. Phokha, S. Pinitsoontorn, S. Maensiri, Structure and magnetic properties of monodisperse Fe3+-doped CeO2 nanospheres. Nano-Micro Lett. 5(4), 223–233 (2013). doi:10.5101/nml.v5i4.p223-233
- M.S. Si, D.Q. Gao, D.Z. Yang, Y. Peng, Z.Y. Zhang, D.S. Xue, Y.S. Liu, X.H. Deng, G.P. Zhang, Intrinsic ferromagnetism in hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets. J. Chem. Phys. 140, 204701 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4879055
- C. Klein, R. Ramchal, A.K. Schmid, M. Farle, Controlling the kinetic order of spin-reorientation transitions in Ni/Cu(100) films by tuning the substrate step structure. Phys. Rev. B 75, 193405 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.193405
- S. Qin, D. Liu, Z. Zuo, Y. Sang, H. Liu, UV-irradiation-enhanced ferromagnetism in BaTiO3. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1(1), 238–241 (2010). doi:10.1021/jz900131x
- L. Feng, D.T. Hoang, C.K. Tsung, W.Y. Huang, S.H.Y. Lo, J.B. Wood, H. Wang, J.Y. Tang, P.D. Yang, Catalytic properties of Pt cluster-decorated CeO2 nanostructures. Nano Res. 4(1), 61–71 (2011). doi:10.1007/s12274-010-0042-4
- G. Kresse, J. Furthmuller, Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54(16), 11169–11186 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169
- D.A. Andersson, S.I. Simak, N.V. Skorodumova, I.A. Abrikosov, B. Johansson, Theoretical study of CeO2 doped with tetravalent ions. Phys. Rev. B 76(17), 174119 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.76.174119
- M. Nolan, S.C. Parker, G.W. Watson, The electron structure of oxygen vacancy defects at the low index surfaces of ceria. Surf. Sci. 595(1–3), 223–232 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.susc.2005.08.015
- C. Loschen, J. Carrasco, K.M. Neyman, F. Illas, First-principles LDA+U and GGA+U study of cerium oxides: dependence on the effective U parameter. Phys. Rev. B 75, 035115 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.035115
- J. Li, Z. Chen, X.X. Wang, D.M. Proderpio, A novel two-dimensional mercury antimony telluride: low temperature synthesis and characterization of RbHgSbTe3. J. Alloys Compd. 262, 28–33 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(97)00324-1
- J. Xu, C.G. Hu, Y. Xi, C. Peng, B.Y. Wan, X.S. He, Synthesis, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of barium vanadate nanoflowers. Mater. Res. Bull. 46(6), 946–950 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.02.023
- X.A. Huang, D. Kocaefe, Y. Kocaefe, Y. Boluk, A. Pichette, A spectrocolorimetric and chemical study on color modification of heat-treated wood during artificial weathering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(14), 5360–5369 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.02.005
- D.C. Cronemeyer, Infrared absorption of reduced rutile TiO2 single crystals. Phys. Rev. 113(5), 1222–1226 (1959). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.113.1222
- D.L. Guo, C.G. Hu, Y. Xi, UV-irradiation-enhanced ferromagnetism of barium vanadate (Ba3V2O8) nanoflowers. J. Alloy. Compd. 550, 389–394 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.152
- X.H. Lu, X. Huang, S.L. Xie, D.Z. Zheng, Z.Q. Liu, C.L. Liang, Y.X. Tong, Facile electrochemical synthesis of single crystalline CeO2 octahedrons and their optical properties. Langmuir 26(10), 7569–7573 (2010). doi:10.1021/la904882t
- A. Arumugam, C. Karthikeyan, A.S.H. Hameed, K. Gopinath, S. Gowri, V. Karthika, Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 49, 408–415 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.042
- L.N. Wang, F.M. Meng, Oxygen vacancy and Ce3+ ion dependent magnetism of monocrystal CeO2 nanopoles synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(9), 3492–3498 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.036
- Z. Zhang, C. Hu, M. Hashim, P. Chen, Y. Xiong, C. Zhang, Synthesis and magnetic properties of FeMoO4 nanorods. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176(9), 756–761 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2011.02.018
- X.Y. Wu, J. Du, H.B. Li, M.F. Zhang, B.J. Fan, Y.C. Zhu, Y.T. Qian, Aqueous mineralization process to synthesize uniform shuttle-like BaMoO4 microcrystals at room temperature. J. Solid State Chem. 180(11), 3288–3295 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2007.07.010
- G. Kresse, D. Joubert, From ultrasoft pseudopotential to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59(3), 1758–1775 (1999). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758
- J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(18), 3865–3868 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.386
- J.B. Goodenough, Magnetism and the Chemical Bond (Interscience, New York, 1963)
- S. Yamanaka, K. Koizumi, Y. Kitagawa, T. Kawakami, M. Okumura, K. Yamaguchi, Chemical bonding, less screening, and Hund’s rule revisted. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 105(6), 687–700 (2005). doi:10.1002/qua.20784
References
X.L. Wang, S.Z. Yi, E.W. Liang, Y.Y. Wu, Z.X. Fang, Study on preparation of polishing powder for LCD. Adv. Mater. Res. 785–786, 480–483 (2013). doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.785-786.480
Y. Chen, Z.N. Li, N.M. Miao, Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)/CeO2 hybrid particles for enhanced chemical mechanical polishing performance. Tribol. Int. 82, 211–217 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2014.10.013
M. Ozawa, Role of cerium-zirconium mixed oxides as catalysts for car pollution: a short review. J. Alloy. Compd. 275, 886–890 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(98)00477-0
S.Y. Christou, S. Garacia-Rodriguez, J.L.G. Fierro, A.M. Efstathiou, Deactivation of Pd/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 model three-way catalyst by P, Ca and Zn deposition. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 111, 233–245 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.10.004
Z.X. Yang, X.H. Yu, Z.S. Lu, S.F. Li, K. Hermansson, Oxygen vacancy pairs on CeO2 (110): a DFT+U study. Phys. Lett. A 373(31), 2786–2792 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2009.05.055
K.C. Anjaneya, G.P. Nayaka, J. Manjanna, G. Govindaraj, K.N. Ganesha, Preparation and characterization of Ce1-xGdxO2-delta (x = 0.1–0.3) as solid electrolyte for intermediate temperature SOFC. J. Alloy. Compd. 578, 53–59 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.05.010
E. Bekyarova, P. Fornasiero, J. Kaspar, M. Graziani, CO oxidation on Pd/CeO2-ZrO2 catalysts. Catal. Today 45(1–4), 179–183 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00212-0
H. Yahiro, Y. Baba, K. Eguchi, H. Arai, High-temperature fuel-cell with ceria-yttria solid electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135(8), 2077–2080 (1988). doi:10.1149/1.2096212
M.F. Al-Kuhaili, S.M.A. Durrani, I.A. Bakhtiari, Carbon monoxide gas-sensing of CeO2-ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255(5), 3033–3039 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.08.058
B. Choudhury, A. Choudhury, Ce3+ and oxygen vacancy mediated tuning of structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 131(3), 666–671 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.10.032
Y. Taga, Recent progress in coating technology for surface modification of automotive glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 218, 335–341 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(97)00281-0
S. Zec, S. Boskovic, B. Kaluderovic, Z. Bogdanov, N. Popovic, Chemical reduction of nanocrystalline CeO2. Ceram. Int. 35(1), 195–198 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2007.10.031
L. Zhang, H. Jiang, M. Selke, X.M. Wang, Selective cytotoxicity effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles under UV irradiation. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 10(2), 278–286 (2014). doi:10.1166/jbn.2014.1790
R. Si, M. Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, Shape and crystal-plane effects of nanoscale ceria on the activity of Au-CeO2 catalysts for the water-gas shift reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 47(15), 2884–2887 (2008). doi:10.1002/anie.200705828
N. Izu, S. Nishizaki, T. Itoh, M. Nishibori, W. Shin, I. Matsubara, Gas response, response time and selectivity of a resistive CO sensor based on two connected CeO2 thick films with various particles sizes. Sens. Actuators B 136(2), 364–370 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.snb.2008.12.018
M. Nolan, Hybrid density functional theory description of oxygen vacancies in the CeO2 (110) and (100). Chem. Phys. Lett. 499(1–3), 126–130 (2010). doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2010.09.016
X.P. Han, J.C. Lee, H.I. Yoo, Oxygen-vacancy-induced ferromagnetism in CeO2 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B 79(10), 100403 (2009). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.79.100403
S. Phokha, S. Pinitsoontorn, S. Maensiri, Structure and magnetic properties of monodisperse Fe3+-doped CeO2 nanospheres. Nano-Micro Lett. 5(4), 223–233 (2013). doi:10.5101/nml.v5i4.p223-233
M.S. Si, D.Q. Gao, D.Z. Yang, Y. Peng, Z.Y. Zhang, D.S. Xue, Y.S. Liu, X.H. Deng, G.P. Zhang, Intrinsic ferromagnetism in hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets. J. Chem. Phys. 140, 204701 (2014). doi:10.1063/1.4879055
C. Klein, R. Ramchal, A.K. Schmid, M. Farle, Controlling the kinetic order of spin-reorientation transitions in Ni/Cu(100) films by tuning the substrate step structure. Phys. Rev. B 75, 193405 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.193405
S. Qin, D. Liu, Z. Zuo, Y. Sang, H. Liu, UV-irradiation-enhanced ferromagnetism in BaTiO3. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1(1), 238–241 (2010). doi:10.1021/jz900131x
L. Feng, D.T. Hoang, C.K. Tsung, W.Y. Huang, S.H.Y. Lo, J.B. Wood, H. Wang, J.Y. Tang, P.D. Yang, Catalytic properties of Pt cluster-decorated CeO2 nanostructures. Nano Res. 4(1), 61–71 (2011). doi:10.1007/s12274-010-0042-4
G. Kresse, J. Furthmuller, Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54(16), 11169–11186 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169
D.A. Andersson, S.I. Simak, N.V. Skorodumova, I.A. Abrikosov, B. Johansson, Theoretical study of CeO2 doped with tetravalent ions. Phys. Rev. B 76(17), 174119 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.76.174119
M. Nolan, S.C. Parker, G.W. Watson, The electron structure of oxygen vacancy defects at the low index surfaces of ceria. Surf. Sci. 595(1–3), 223–232 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.susc.2005.08.015
C. Loschen, J. Carrasco, K.M. Neyman, F. Illas, First-principles LDA+U and GGA+U study of cerium oxides: dependence on the effective U parameter. Phys. Rev. B 75, 035115 (2007). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.035115
J. Li, Z. Chen, X.X. Wang, D.M. Proderpio, A novel two-dimensional mercury antimony telluride: low temperature synthesis and characterization of RbHgSbTe3. J. Alloys Compd. 262, 28–33 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(97)00324-1
J. Xu, C.G. Hu, Y. Xi, C. Peng, B.Y. Wan, X.S. He, Synthesis, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of barium vanadate nanoflowers. Mater. Res. Bull. 46(6), 946–950 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.02.023
X.A. Huang, D. Kocaefe, Y. Kocaefe, Y. Boluk, A. Pichette, A spectrocolorimetric and chemical study on color modification of heat-treated wood during artificial weathering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(14), 5360–5369 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.02.005
D.C. Cronemeyer, Infrared absorption of reduced rutile TiO2 single crystals. Phys. Rev. 113(5), 1222–1226 (1959). doi:10.1103/PhysRev.113.1222
D.L. Guo, C.G. Hu, Y. Xi, UV-irradiation-enhanced ferromagnetism of barium vanadate (Ba3V2O8) nanoflowers. J. Alloy. Compd. 550, 389–394 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.10.152
X.H. Lu, X. Huang, S.L. Xie, D.Z. Zheng, Z.Q. Liu, C.L. Liang, Y.X. Tong, Facile electrochemical synthesis of single crystalline CeO2 octahedrons and their optical properties. Langmuir 26(10), 7569–7573 (2010). doi:10.1021/la904882t
A. Arumugam, C. Karthikeyan, A.S.H. Hameed, K. Gopinath, S. Gowri, V. Karthika, Synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles using Gloriosa superba L. leaf extract and their structural, optical and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 49, 408–415 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.042
L.N. Wang, F.M. Meng, Oxygen vacancy and Ce3+ ion dependent magnetism of monocrystal CeO2 nanopoles synthesized by a facile hydrothermal method. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(9), 3492–3498 (2013). doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.05.036
Z. Zhang, C. Hu, M. Hashim, P. Chen, Y. Xiong, C. Zhang, Synthesis and magnetic properties of FeMoO4 nanorods. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 176(9), 756–761 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2011.02.018
X.Y. Wu, J. Du, H.B. Li, M.F. Zhang, B.J. Fan, Y.C. Zhu, Y.T. Qian, Aqueous mineralization process to synthesize uniform shuttle-like BaMoO4 microcrystals at room temperature. J. Solid State Chem. 180(11), 3288–3295 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2007.07.010
G. Kresse, D. Joubert, From ultrasoft pseudopotential to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 59(3), 1758–1775 (1999). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(18), 3865–3868 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.386
J.B. Goodenough, Magnetism and the Chemical Bond (Interscience, New York, 1963)
S. Yamanaka, K. Koizumi, Y. Kitagawa, T. Kawakami, M. Okumura, K. Yamaguchi, Chemical bonding, less screening, and Hund’s rule revisted. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 105(6), 687–700 (2005). doi:10.1002/qua.20784