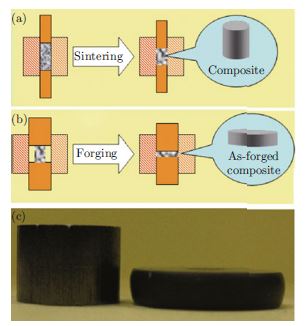
Superplastic Behavior of Alumina Composites Mediated by Carbon Nanotubes
Corresponding Author: Qing Huang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 5 No. 3 (2013), Article Number: 174-181
Abstract
The high temperature creep behavior of carbon nanotube (CNT)/alumina was mediated by the surface chemical functionalization used for synthesis of composite powders. Non-covalent functionalized carbon nanotubes make composites ductile, but covalent approach leads composites that are creep-resistant. Oxygen vacancy mechanism is proposed to account for this mediation effect in this communication.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- J. W. Edington, K. N. Melton and C. P. Cutler, “Superplasticity”, Prog. Mater. Sci. 21(2), 63–170 (1976). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0079-6425(76)90005-0
- I. A. Ovid’ko, “Nanodefects in nanostructures”, Phil. Mag. Lett. 83(10), 611–20 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09500830310001593463
- F. Wakai, “Superplasticity of ceramics”, Ceram. Int. 17(3), 153–63 (1991). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0272-8842(91)90062-5
- F. Wakai, N. Kondo, H. Ogawa, T. Nagano and S. Tsurekawa, “Ceramics superplasticity: Deformation mechanisms and microstructures”, Mater. Charact. 37(5), 331–41 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1044-5803(96)00174-X
- Amiya K. Mukherjee, “The rate controlling mechanism in superplasticity”, Mate. Sci. Eng. 8(2), 83–89 (1971). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(71)90085-1
- R. Raj, “Model for interface reaction control in superplastic deformation of non-stoichiometric ceramics”, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. 166(1-2), 89–95 (1993). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(93)90313-4
- Q. Huang, Y. S. Bando, X. Xu, T. Nishimura, C. Y. Zhi, C. C. Tang, F. F. Xu, L. Gao and D. Golberg, “Enhancing superplasticity of engineering ceramics by introducing BN nanotubes”, Nanotechnology, 18(48), 485706 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/48/485706
- E. Zapata-Solvas, R. Poyato, D. Gomez-Garcia, A. Dominguez-Rodriguez, V. Radmilovic and N. P. Padture, “Creep-resistant composites of alumina and single-wall carbon nanotubes”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92(11), 11912 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/+10.1063/1.2899945
- A. Bataille, J. Crampon, and R. Duclos, “Upgrading superplastic deformation performance of fine-grained alumina by graphite particles”, Ceram. Int., 25(3), 215–222 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0272-8842(98)00026-1
- P. Lu, Q. Huang, D. T. Jiang, B. Ding, Y. L. Hsieh, I. A. Ovid’ko and A. Mukherjee, “Highly dispersive carbon nanotube/alumina composites and their electrospun nanofibers”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92(11), 2583–2589 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03283.x
- G. D. Zhan, J. Kuntz, J. Wan, J. Garay and A. K. Mukherjee, “A novel processing route to develop a dense nanocrystalline alumina matrix (<100 nm) nanocomposite material”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86(1), 200–202 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2003.tb03306.x
- M. L. Toebes, T. A. Nijhuis, J. Hajek, J. H. Bitter, A. J. van Dillen, D. Y. Murzin and K. P. de Jong, “Support effects in hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde over carbon nanofiber-supported platinum catalysts: Kinetic modeling”, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60(21), 5682–5695 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2005.05.031
- Q. Huang, D. T. Jiang, I. A. Ovid’ko and A. Mukherjee, “High current induced damage on carbon nanotubes: case in spark plasma sintering”, Script Mater. 63(12), 1181–1184 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.08.030
- E. G. Yukihara and S. W. S. McKeever, “Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dosimetry in medicine”, Phys. Med. Biol. 53(20), R351–R379 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/53/20/R01
- L. A. Xue and I. W. Chen, “Superplastic alumina at temperatures below 1300°C using charge-compensating dopants”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79(1), 233–238 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1996.tb07903.x
- X. B. Yang, H. J. Li, Q. Y. Bi, Y. Cheng, Q. Tang, X. B. Qian and J. Xu, “Growth of a-Al2O3:C crystal with highly sensitive optically stimulated luminescence”, J. Lumin. 129(5), 566–569 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2008.12.015
- D. T. Jiang, D. M. Hulbert, J. D. Kuntz, U. Anselmi-Tamburini and A. K. Mukherjee, “Spark plasma sintering: A high strain rate low temperature forming tool for ceramics”, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. 463(1-2), 89–93 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.163
References
J. W. Edington, K. N. Melton and C. P. Cutler, “Superplasticity”, Prog. Mater. Sci. 21(2), 63–170 (1976). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0079-6425(76)90005-0
I. A. Ovid’ko, “Nanodefects in nanostructures”, Phil. Mag. Lett. 83(10), 611–20 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/09500830310001593463
F. Wakai, “Superplasticity of ceramics”, Ceram. Int. 17(3), 153–63 (1991). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0272-8842(91)90062-5
F. Wakai, N. Kondo, H. Ogawa, T. Nagano and S. Tsurekawa, “Ceramics superplasticity: Deformation mechanisms and microstructures”, Mater. Charact. 37(5), 331–41 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1044-5803(96)00174-X
Amiya K. Mukherjee, “The rate controlling mechanism in superplasticity”, Mate. Sci. Eng. 8(2), 83–89 (1971). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(71)90085-1
R. Raj, “Model for interface reaction control in superplastic deformation of non-stoichiometric ceramics”, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. 166(1-2), 89–95 (1993). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(93)90313-4
Q. Huang, Y. S. Bando, X. Xu, T. Nishimura, C. Y. Zhi, C. C. Tang, F. F. Xu, L. Gao and D. Golberg, “Enhancing superplasticity of engineering ceramics by introducing BN nanotubes”, Nanotechnology, 18(48), 485706 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/48/485706
E. Zapata-Solvas, R. Poyato, D. Gomez-Garcia, A. Dominguez-Rodriguez, V. Radmilovic and N. P. Padture, “Creep-resistant composites of alumina and single-wall carbon nanotubes”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 92(11), 11912 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/+10.1063/1.2899945
A. Bataille, J. Crampon, and R. Duclos, “Upgrading superplastic deformation performance of fine-grained alumina by graphite particles”, Ceram. Int., 25(3), 215–222 (1999). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0272-8842(98)00026-1
P. Lu, Q. Huang, D. T. Jiang, B. Ding, Y. L. Hsieh, I. A. Ovid’ko and A. Mukherjee, “Highly dispersive carbon nanotube/alumina composites and their electrospun nanofibers”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92(11), 2583–2589 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.03283.x
G. D. Zhan, J. Kuntz, J. Wan, J. Garay and A. K. Mukherjee, “A novel processing route to develop a dense nanocrystalline alumina matrix (<100 nm) nanocomposite material”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 86(1), 200–202 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2003.tb03306.x
M. L. Toebes, T. A. Nijhuis, J. Hajek, J. H. Bitter, A. J. van Dillen, D. Y. Murzin and K. P. de Jong, “Support effects in hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde over carbon nanofiber-supported platinum catalysts: Kinetic modeling”, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60(21), 5682–5695 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2005.05.031
Q. Huang, D. T. Jiang, I. A. Ovid’ko and A. Mukherjee, “High current induced damage on carbon nanotubes: case in spark plasma sintering”, Script Mater. 63(12), 1181–1184 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.08.030
E. G. Yukihara and S. W. S. McKeever, “Optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dosimetry in medicine”, Phys. Med. Biol. 53(20), R351–R379 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/53/20/R01
L. A. Xue and I. W. Chen, “Superplastic alumina at temperatures below 1300°C using charge-compensating dopants”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79(1), 233–238 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1996.tb07903.x
X. B. Yang, H. J. Li, Q. Y. Bi, Y. Cheng, Q. Tang, X. B. Qian and J. Xu, “Growth of a-Al2O3:C crystal with highly sensitive optically stimulated luminescence”, J. Lumin. 129(5), 566–569 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2008.12.015
D. T. Jiang, D. M. Hulbert, J. D. Kuntz, U. Anselmi-Tamburini and A. K. Mukherjee, “Spark plasma sintering: A high strain rate low temperature forming tool for ceramics”, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. 463(1-2), 89–93 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.163