Algebraic Current-voltage and Voltage Dependent Resistance Expressions for Ballistic Nano Conductors and Their Low Voltage Nonlinearity
Corresponding Author: Serhan YAMACLI
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 5 No. 3 (2013), Article Number: 169-173
Abstract
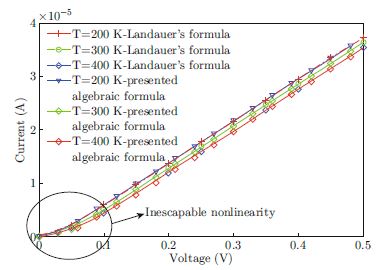
In this study, an algebraic current-voltage (I–V) equation suitable for the hand-calculation of ballistic nano conductors is derived from Landauer’s formulation. A voltage and temperature dependent resistance expression is also obtained. It is shown that the presented algebraic I–V expression and the original Landauer’s formula give the same characteristics as expected. Moreover, the I–V characteristics of ballistic nano conductors are investigated and it is concluded that there is an inescapable nonlinearity originating from the curvature of Fermi-Dirac distribution function in low voltage range. Finally, the total harmonic distortion (THD) of a sample ballistic nano conductor caused from its low voltage nonlinearity is computed via HSPICE simulations.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- G. F. Close and H.-S. P. Wong, “Assembly and electrical characterization of multiwall carbon nanotube interconnects”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 7(5), 596–600 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2008.927373
- S. Kanthamani, N. Srujana Vahini and V. Abhaikumar, “Quasi-static modelling of carbon nanotube interconnects for gigahertz applications”, Micro & Nano Lett. 5(5), 328–332 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2010.0073
- C. Xu, H. Li and K. Banerjee, “Modeling, analysis, and design of graphene nano-ribbon interconnects”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56(8), 1567–1578 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TED.2009.2024254
- H. Li, W.-Y. Yin, K. Banerjee and J.-F. Mao, “Circuit modeling and performance analysis of multi-walled carbon nanotube interconnects”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55(6), 1328–1337 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TED.2008.922855
- S. Mohammadzadeh, D. Pouladsaz, R. Streiter and T. Gessner, “Electronic transport properties in copper nanowire”, Microelectron. Eng. 85(10), 1992–1994 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2008.06.005
- G. W. Hanson, “Fundamentals of Nanoelectronics”, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, USA, 2007.
- A. Naeemi, J. D. Meindl, “Compact physics-based circuit models for graphene nanoribbon interconnects”, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 56(9), 1882–1833 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TED.2009.2026122
- S. Datta, “Quantum Transport: Atom to Transistor”, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139164313
- C. Durkan, “Current at the Nanoscale: An Introduction to Nanoelectronics”, Imperial College Press, London, UK, 2007.
- P. Avouris, “Carbon Nanotube Electronics”, Proceedings of the IEEE 91(11), 1772–1884 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2003.818338
- I. M. Kastnelson, “Minimal vonductivity in bilayer graphene”, Eur. Phys. J. B 52(2), 151–153 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2006-00294-6
- H. Ohnishi, Y. Kondo and K. Takayanagi, “Quantized conductance through individual rows of suspended gold atoms”, Nature 395, 78–783 (1998). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/27399
- P. J. Burke, “Lüttinger liquid theory as a model of the gigahertz electrical properties of carbon nanotubes”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 1(3), 129–144 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2002.806823
- Z. Xu, Q. S. Zheng and G. H. Chen, “Elementary building blocks of graphene-nanoribbon-based electronic devices”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(22), 223115 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2745268
- Y. Mokrusov, G. Bihlmayer and S. Blugel, “Full-potential linearized augmented plane-wave method for one-dimensional systems: Gold nanowire and iron monowires in a gold tube”, Phys. Rev. B 72(4), 045402 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.045402
- H. Kajiura, A. Nandyala, U. C. Coskun, A. Bezryadin, M. Shiraishi and A. Ata, “Electronic mean free path in as-produced and purified single-wall carbon nanotubes”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(12), 122106 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1885189
- S. Weingart, C. Bock, U. Kunze, F. Speck, Th Seyller and L. Ley, “Low-temperature ballistic transport in nanoscale epitaxial graphene cross junctions”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(26), 262101 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3276560
- E. C. Walter, M. P. Zach, F. Favier, B. J. Murray, K. Inazu, J. C. Hemminger and R. M. Penner, “Metal nanowire arrays by electrodeposition”, Chem. Phys. Chem. 14(2), 131–138 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200390022
- International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) Roadmap, 2013, http://www.itrs.net/
- G. Rubio, N. Agrait and S. Vieira, “Atomic-sized metallic contacts: mechanical properties and electronic transport”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(13), 2302–2305 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.2302
- C. Z. Li, “Quantum transport in metallic nanowires fabricated by electrochemical deposition/dissolution”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 894–896 (1998). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.120928
- J. A. Nesteroff, Y. V. Pershin and V. Privman, “Influence of nuclear spin polarization on quantum wire conductance”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 4(1), 141–147 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2004.837855
- Y. Awano, S. Shintaro, M. Nihei, S. Tadashi, Y. Ohno and M. Takashi, “Carbon nanotubes for VLSI: interconnect and transistor applications”, Proceedings of the IEEE 98, 2015–2031 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2068030
- A. Svizhenko, M. P. Anantram and T. R. Govindan, “Ballistic transport and electrostatics in metallic carbon nanotubes”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 4(5), 557–562 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2005.851409
References
G. F. Close and H.-S. P. Wong, “Assembly and electrical characterization of multiwall carbon nanotube interconnects”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 7(5), 596–600 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2008.927373
S. Kanthamani, N. Srujana Vahini and V. Abhaikumar, “Quasi-static modelling of carbon nanotube interconnects for gigahertz applications”, Micro & Nano Lett. 5(5), 328–332 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1049/mnl.2010.0073
C. Xu, H. Li and K. Banerjee, “Modeling, analysis, and design of graphene nano-ribbon interconnects”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56(8), 1567–1578 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TED.2009.2024254
H. Li, W.-Y. Yin, K. Banerjee and J.-F. Mao, “Circuit modeling and performance analysis of multi-walled carbon nanotube interconnects”, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 55(6), 1328–1337 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TED.2008.922855
S. Mohammadzadeh, D. Pouladsaz, R. Streiter and T. Gessner, “Electronic transport properties in copper nanowire”, Microelectron. Eng. 85(10), 1992–1994 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2008.06.005
G. W. Hanson, “Fundamentals of Nanoelectronics”, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey, USA, 2007.
A. Naeemi, J. D. Meindl, “Compact physics-based circuit models for graphene nanoribbon interconnects”, IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 56(9), 1882–1833 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TED.2009.2026122
S. Datta, “Quantum Transport: Atom to Transistor”, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139164313
C. Durkan, “Current at the Nanoscale: An Introduction to Nanoelectronics”, Imperial College Press, London, UK, 2007.
P. Avouris, “Carbon Nanotube Electronics”, Proceedings of the IEEE 91(11), 1772–1884 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2003.818338
I. M. Kastnelson, “Minimal vonductivity in bilayer graphene”, Eur. Phys. J. B 52(2), 151–153 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2006-00294-6
H. Ohnishi, Y. Kondo and K. Takayanagi, “Quantized conductance through individual rows of suspended gold atoms”, Nature 395, 78–783 (1998). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/27399
P. J. Burke, “Lüttinger liquid theory as a model of the gigahertz electrical properties of carbon nanotubes”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 1(3), 129–144 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2002.806823
Z. Xu, Q. S. Zheng and G. H. Chen, “Elementary building blocks of graphene-nanoribbon-based electronic devices”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(22), 223115 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2745268
Y. Mokrusov, G. Bihlmayer and S. Blugel, “Full-potential linearized augmented plane-wave method for one-dimensional systems: Gold nanowire and iron monowires in a gold tube”, Phys. Rev. B 72(4), 045402 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.045402
H. Kajiura, A. Nandyala, U. C. Coskun, A. Bezryadin, M. Shiraishi and A. Ata, “Electronic mean free path in as-produced and purified single-wall carbon nanotubes”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(12), 122106 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1885189
S. Weingart, C. Bock, U. Kunze, F. Speck, Th Seyller and L. Ley, “Low-temperature ballistic transport in nanoscale epitaxial graphene cross junctions”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(26), 262101 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3276560
E. C. Walter, M. P. Zach, F. Favier, B. J. Murray, K. Inazu, J. C. Hemminger and R. M. Penner, “Metal nanowire arrays by electrodeposition”, Chem. Phys. Chem. 14(2), 131–138 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200390022
International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS) Roadmap, 2013, http://www.itrs.net/
G. Rubio, N. Agrait and S. Vieira, “Atomic-sized metallic contacts: mechanical properties and electronic transport”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(13), 2302–2305 (1996). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.2302
C. Z. Li, “Quantum transport in metallic nanowires fabricated by electrochemical deposition/dissolution”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 894–896 (1998). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.120928
J. A. Nesteroff, Y. V. Pershin and V. Privman, “Influence of nuclear spin polarization on quantum wire conductance”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 4(1), 141–147 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2004.837855
Y. Awano, S. Shintaro, M. Nihei, S. Tadashi, Y. Ohno and M. Takashi, “Carbon nanotubes for VLSI: interconnect and transistor applications”, Proceedings of the IEEE 98, 2015–2031 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2010.2068030
A. Svizhenko, M. P. Anantram and T. R. Govindan, “Ballistic transport and electrostatics in metallic carbon nanotubes”, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 4(5), 557–562 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2005.851409