Indocyanine Green Nanoparticles for Theranostic Applications
Corresponding Author: Lintao Cai
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 5 No. 3 (2013), Article Number: 145-150
Abstract
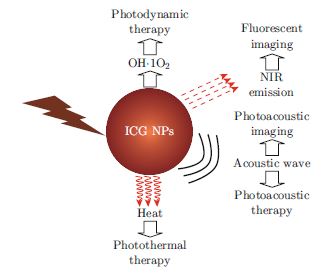
Theranostics is a concept that integrated imaging and therapy. As an emerging field, it embraces multiple techniques to arrive at an individualized treatment purpose. Indocyanine green (ICG) is a near infrared dye that has been approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in USA for the use in indicator-dilution studies in humans. ICG nanoparticles (NPs) have attracted much attention for its potential applications in cancer theranostics. This review focuses on the preparation, application of ICG NPs for in vivo imaging (fluorescent imaging and photoacoustic imaging) and therapeutics (photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy and photoacoustic therapy), and future directions based on recent developments in these areas. It is hoped that this review might provide new impetus to understand ICG NPs for cancer theranostics.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- X. Y. Chen, S. S. Gambhir and J. Cheon, “Theranostic nanomedicine”, Acc. Chem. Res. 44(10), 841–841 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar200231d
- K. Y. Choi, G. Liu, S. Lee and X. Y. Chen, “Theranostic nanoplatforms for simultaneous cancer imaging and therapy: current approaches and future perspectives”, Nanoscale 4, 330–342 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c1nr11277e
- T. Lammers, S. Aime, W. E. Hennink, G. Storm and F. Kiessling, “Theranostic Nanomedicine”, Acc. Chem. Res. 44(10), 1029–1038 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar200019c
- J. V. Jokerst and S. S. Gambhir, “Molecular Imaging with Theranostic Nanoparticles”, Acc Chem Res 44(10), 1050–1060 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar200106e
- W. S. Kuo, Y. T. Chang, K. C. Cho, K. C. Chiu, C. H. Lien, C. S. Yeh and S. J. Chen, “Gold nanomaterials conjugated with indocyanine green for dual-modality photodynamic and photothermal therapy”, Biomaterials 33(11), 3270–3278 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.035
- B. M. Barth, E. I. Altinoglu, S. S. Shanmugavelandy, J. M. Kaiser, D. Crespo-Gonzalez, N. A. DiVittore, C. McGovern, T. M. Goff, N. R. Keasey, J. H. Adair, T. P. Loughran, Jr., D. F. Claxton and M. Kester, “Targeted indocyanine-green-loaded calcium phosphosilicate nanoparticles for in vivo photodynamic therapy of leukemia”, Acs Nano 5(7), 5325–5337 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn2005766
- G. Kim, S. W. Huang, K. C. Day, M. O’Donnell, R. R. Agayan, M. A. Day, R. Kopelman and S. Ashkenazi, “Indocyanine-green-embedded PEBBLEs as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging”, J. Biomed. Opt. 12(4), 044020 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.2771530
- X. Zheng, D. Xing, F. Zhou, B. Wu and W. R. Chen, “Indocyanine green-containing nanostructure as near infrared dual-functional targeting probes for optical imaging and photothermal therapy”, Mol. Pharm. 8(2), 447–456 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp100301t
- V. Saxena, M. Sadoqi and J. Shao, “Enhanced photo-stability, thermal-stability and aqueous-stability of indocyanine green in polymeric nanoparticulate systems”, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 74(1), 29–38 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2004.01.002
- L. Larush and S. Magdassi, “Formation of near-infrared fluorescent nanoparticles for medical imaging”, Nanomedicine 6(2), 233–240 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/nnm.11.5
- A. J. Gomes, L. O. Lunardi, J. M. Marchetti, C. N. Lunardi and A. C. Tedesco, “Indocyanine green nanoparticles useful for photomedicine”, Photomedicine and Laser Surgery 24(4), 514–521 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/pho.2006.24.514
- D. Grosenick, H. Wabnitz and B. Ebert, “Recent advances in contrast-enhanced near infrared diffuse optical imaging of diseases using indocyanine green”, J. Near Infrared Spec. 20(1), 203–221 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.964
- B. M. Barth, R. Sharma, E. I. Altinoglu, T. T. Morgan, S. S. Shanmugavelandy, J. M. Kaiser, C. McGovern, G. L. Matters, J. P. Smith, M. Kester and J. H. Adair, “Bioconjugation of calcium phosphosilicate composite nanoparticles for selective targeting of human breast and pancreatic cancers in vivo”, Acs Nano 4(3), 1279–1287 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn901297q
- J. Yu, M. A. Yaseen, B. Anvari and M. S. Wong, “Synthesis of near-infrared-absorbing nanoparticle-assembled capsules”, Chem. Mater. 19(6), 1277–1284 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cm062080x
- V. Saxena, M. Sadoqi and J. Shao, “Indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles: preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro release”, Int. J. Pharm. 278(2), 293–301 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.03.032
- R. H. Patel, A. S. Wadajkar, N. L. Patel, V. C. Kavuri, K. T. Nguyen and H. Liu, “Multifunctionality of indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles for enhanced optical imaging and hyperthermia intervention of cancer”, J. Biomed. Opt. 17(4), 046003 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.17.4.046003
- X. Zheng, D. Xing, F. Zhou, B. Wu and W. R. Chen, “Indocyanine green-containing nanostructure as near infrared dual-functional targeting probes for optical imaging and photothermal therapy”, Mol. Pharm. 8(2), 447–456 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp100301t
- H. Kim, Y. Chen, C. W. Mount, W. R. Gombotz, X. Li and S. H. Pun, “Evaluation of temperature-sensitive, indocyanine green-encapsulating micelles for noninvasive near-infrared tumor imaging”, Pharm. Res. 27(9), 1900–1913 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0190-y
- G. Kim, S. W. Huang, K. C. Day, M. O’Donnell, R. R. Agayan, M. A. Day, R. Kopelman and S. Ashkenazi, “Indocyanine-green-embedded PEBBLEs as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging”, J. Biomed. Opt. 12(4), 044020 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.2771530
- D. K. Bwambok, B. El-Zahab, S. K. Challa, M. Li, L. Chandler, G. A. Baker and I. M. Warner, “Near-infrared fluorescent nanoGUMBOS for biomedical imaging”, Acs Nano 3(12), 3854–3860 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn9010126
- B. Bahmani, S. Gupta, S. Upadhyayula, V. I. Vullev and B. Anvari, “Effect of polyethylene glycol coatings on uptake of indocyanine green loaded nanocapsules by human spleen macrophages in vitro”, J. Biomed. Opt. 16(5), 051303 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.3574761
- C. F. Zheng, M. B. Zheng, P. Gong, D. X. Jia, P. F. Zhang, B. H. Shi, Z. H. Sheng, Y. F. Ma and L. T. Cai, “Indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable tumor targeting nanoprobes for in vitro and in vivo imaging”, Biomaterials 33(22), 5603–5609 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.044
- M. Zheng, C. Yue, Y. Ma, P. Gong, P. Zhao, C. Zheng, Z. Sheng, P. Zhang, Z. Wang and L. Cai, “Single-step assembly of DOX-ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy”, Acs Nano 7(3), 2056–2067 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn400334y
- J. Zhong, S. Yang, X. Zheng, T. Zhou and D. Xing, “In vivo photoacoustic therapy with cancer-targeted indocyanine green-containing nanoparticles”, Nanomedicine 8(6), 903–919 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/NNM.12.123
- J. Yu, D. Javier, M. A. Yaseen, N. Nitin, R. Richards-Kortum, B. Anvari and M. S. Wong, “Self-assembly synthesis, tumor cell targeting, and photothermal capabilities of antibody-coated indocyanine green nanocapsules”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(6), 1929–1938 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja908139y
- M. A. Yaseen, J. Yu, B. Jung, M. S. Wong and B. Anvari, “Biodistribution of encapsulated indocyanine green in healthy mice”, Mol. Pharm. 6(5), 1321–1332 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp800270t
- P. Sharma, N. E. Bengtsson, G. A. Walter, H. B. Sohn, G. Zhou, N. Iwakuma, H. Zeng, S. R. Grobmyer, E. W. Scott and B. M. Moudgil, “Adolinium-doped silica nanoparticles encapsulating indocyanine green for near infrared and magnetic resonance imaging”, Small 8(18), 2856–2868 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200258
- B. Quan, K. Choi, Y. H. Kim, K. W. Kang and D. S. Chung, “Near infrared dye indocyanine green doped silica nanoparticles for biological imaging”, Talanta 99, 387–393 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.069
- C.-H. Lee, S.-H. Cheng, Y.-J. Wang, Y.-C. Chen, N.-T. Chen, J. Souris, C.-T. Chen, C.-Y. Mou, C.-S. Yang and L.-W. Lo, “Near-infrared mesoporous silica nanoparticles for optical imaging: characterization and in vivo biodistribution”, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19(2), 215–222 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200800753
- E. I. Altinoglu, T. J. Russin, J. M. Kaiser, B. M. Barth, P. C. Eklund, M. Kester and J. H. Adair, “Near-infrared emitting fluorophore-doped calcium phosphate nanoparticles for in vivo imaging of human breast cancer”, Acs Nano 2(10), 2075–2084 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn800448r
- K. Sano, T. Nakajima, K. Miyazaki, Y. Ohuchi, T. Ikegami, P. L. Choyke and H. Kobayashi, “Short PEG-linkers improve the performance of targeted, activatable monoclonal antibody-indocyanine green optical imaging probes”, Bioconjug. Chem. 24(5), 811–816 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bc400050k
- H. Mok, H. Jeong, S. J. Kim and B. H. Chung, “Indocyanine green encapsulated nanogels for hyaluronidase activatable and selective near infrared imaging of tumors and lymph nodes”, Chem. Commun. (Camb) 48, 8628–8630 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2cc33555g
- P. Rungta, Y. P. Bandera, R. D. Roeder, Y. Li, W. S. Baldwin, D. Sharma, M. G. Sehorn, I. Luzinov and S. H. Foulger, “Selective imaging and killing of cancer cells with protein-activated near-infrared fluorescing nanoparticles”, Macromol. Biosci. 11(7), 927–937 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201100043
- M. A. Daniele, M. L. Shaughnessy, R. Roeder, A. Childress, Y. P. Bandera and S. Foulger, “Magnetic nanoclusters exhibiting protein-activated near-infrared fluorescence”, Acs Nano 7(1), 203–213 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn3037368
References
X. Y. Chen, S. S. Gambhir and J. Cheon, “Theranostic nanomedicine”, Acc. Chem. Res. 44(10), 841–841 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar200231d
K. Y. Choi, G. Liu, S. Lee and X. Y. Chen, “Theranostic nanoplatforms for simultaneous cancer imaging and therapy: current approaches and future perspectives”, Nanoscale 4, 330–342 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c1nr11277e
T. Lammers, S. Aime, W. E. Hennink, G. Storm and F. Kiessling, “Theranostic Nanomedicine”, Acc. Chem. Res. 44(10), 1029–1038 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar200019c
J. V. Jokerst and S. S. Gambhir, “Molecular Imaging with Theranostic Nanoparticles”, Acc Chem Res 44(10), 1050–1060 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ar200106e
W. S. Kuo, Y. T. Chang, K. C. Cho, K. C. Chiu, C. H. Lien, C. S. Yeh and S. J. Chen, “Gold nanomaterials conjugated with indocyanine green for dual-modality photodynamic and photothermal therapy”, Biomaterials 33(11), 3270–3278 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.035
B. M. Barth, E. I. Altinoglu, S. S. Shanmugavelandy, J. M. Kaiser, D. Crespo-Gonzalez, N. A. DiVittore, C. McGovern, T. M. Goff, N. R. Keasey, J. H. Adair, T. P. Loughran, Jr., D. F. Claxton and M. Kester, “Targeted indocyanine-green-loaded calcium phosphosilicate nanoparticles for in vivo photodynamic therapy of leukemia”, Acs Nano 5(7), 5325–5337 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn2005766
G. Kim, S. W. Huang, K. C. Day, M. O’Donnell, R. R. Agayan, M. A. Day, R. Kopelman and S. Ashkenazi, “Indocyanine-green-embedded PEBBLEs as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging”, J. Biomed. Opt. 12(4), 044020 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.2771530
X. Zheng, D. Xing, F. Zhou, B. Wu and W. R. Chen, “Indocyanine green-containing nanostructure as near infrared dual-functional targeting probes for optical imaging and photothermal therapy”, Mol. Pharm. 8(2), 447–456 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp100301t
V. Saxena, M. Sadoqi and J. Shao, “Enhanced photo-stability, thermal-stability and aqueous-stability of indocyanine green in polymeric nanoparticulate systems”, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 74(1), 29–38 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2004.01.002
L. Larush and S. Magdassi, “Formation of near-infrared fluorescent nanoparticles for medical imaging”, Nanomedicine 6(2), 233–240 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/nnm.11.5
A. J. Gomes, L. O. Lunardi, J. M. Marchetti, C. N. Lunardi and A. C. Tedesco, “Indocyanine green nanoparticles useful for photomedicine”, Photomedicine and Laser Surgery 24(4), 514–521 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/pho.2006.24.514
D. Grosenick, H. Wabnitz and B. Ebert, “Recent advances in contrast-enhanced near infrared diffuse optical imaging of diseases using indocyanine green”, J. Near Infrared Spec. 20(1), 203–221 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.964
B. M. Barth, R. Sharma, E. I. Altinoglu, T. T. Morgan, S. S. Shanmugavelandy, J. M. Kaiser, C. McGovern, G. L. Matters, J. P. Smith, M. Kester and J. H. Adair, “Bioconjugation of calcium phosphosilicate composite nanoparticles for selective targeting of human breast and pancreatic cancers in vivo”, Acs Nano 4(3), 1279–1287 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn901297q
J. Yu, M. A. Yaseen, B. Anvari and M. S. Wong, “Synthesis of near-infrared-absorbing nanoparticle-assembled capsules”, Chem. Mater. 19(6), 1277–1284 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cm062080x
V. Saxena, M. Sadoqi and J. Shao, “Indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles: preparation, physicochemical characterization and in vitro release”, Int. J. Pharm. 278(2), 293–301 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.03.032
R. H. Patel, A. S. Wadajkar, N. L. Patel, V. C. Kavuri, K. T. Nguyen and H. Liu, “Multifunctionality of indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles for enhanced optical imaging and hyperthermia intervention of cancer”, J. Biomed. Opt. 17(4), 046003 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.17.4.046003
X. Zheng, D. Xing, F. Zhou, B. Wu and W. R. Chen, “Indocyanine green-containing nanostructure as near infrared dual-functional targeting probes for optical imaging and photothermal therapy”, Mol. Pharm. 8(2), 447–456 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp100301t
H. Kim, Y. Chen, C. W. Mount, W. R. Gombotz, X. Li and S. H. Pun, “Evaluation of temperature-sensitive, indocyanine green-encapsulating micelles for noninvasive near-infrared tumor imaging”, Pharm. Res. 27(9), 1900–1913 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0190-y
G. Kim, S. W. Huang, K. C. Day, M. O’Donnell, R. R. Agayan, M. A. Day, R. Kopelman and S. Ashkenazi, “Indocyanine-green-embedded PEBBLEs as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging”, J. Biomed. Opt. 12(4), 044020 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.2771530
D. K. Bwambok, B. El-Zahab, S. K. Challa, M. Li, L. Chandler, G. A. Baker and I. M. Warner, “Near-infrared fluorescent nanoGUMBOS for biomedical imaging”, Acs Nano 3(12), 3854–3860 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn9010126
B. Bahmani, S. Gupta, S. Upadhyayula, V. I. Vullev and B. Anvari, “Effect of polyethylene glycol coatings on uptake of indocyanine green loaded nanocapsules by human spleen macrophages in vitro”, J. Biomed. Opt. 16(5), 051303 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.3574761
C. F. Zheng, M. B. Zheng, P. Gong, D. X. Jia, P. F. Zhang, B. H. Shi, Z. H. Sheng, Y. F. Ma and L. T. Cai, “Indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable tumor targeting nanoprobes for in vitro and in vivo imaging”, Biomaterials 33(22), 5603–5609 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.04.044
M. Zheng, C. Yue, Y. Ma, P. Gong, P. Zhao, C. Zheng, Z. Sheng, P. Zhang, Z. Wang and L. Cai, “Single-step assembly of DOX-ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemo-photothermal combination therapy”, Acs Nano 7(3), 2056–2067 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn400334y
J. Zhong, S. Yang, X. Zheng, T. Zhou and D. Xing, “In vivo photoacoustic therapy with cancer-targeted indocyanine green-containing nanoparticles”, Nanomedicine 8(6), 903–919 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.2217/NNM.12.123
J. Yu, D. Javier, M. A. Yaseen, N. Nitin, R. Richards-Kortum, B. Anvari and M. S. Wong, “Self-assembly synthesis, tumor cell targeting, and photothermal capabilities of antibody-coated indocyanine green nanocapsules”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(6), 1929–1938 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja908139y
M. A. Yaseen, J. Yu, B. Jung, M. S. Wong and B. Anvari, “Biodistribution of encapsulated indocyanine green in healthy mice”, Mol. Pharm. 6(5), 1321–1332 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp800270t
P. Sharma, N. E. Bengtsson, G. A. Walter, H. B. Sohn, G. Zhou, N. Iwakuma, H. Zeng, S. R. Grobmyer, E. W. Scott and B. M. Moudgil, “Adolinium-doped silica nanoparticles encapsulating indocyanine green for near infrared and magnetic resonance imaging”, Small 8(18), 2856–2868 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200258
B. Quan, K. Choi, Y. H. Kim, K. W. Kang and D. S. Chung, “Near infrared dye indocyanine green doped silica nanoparticles for biological imaging”, Talanta 99, 387–393 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.069
C.-H. Lee, S.-H. Cheng, Y.-J. Wang, Y.-C. Chen, N.-T. Chen, J. Souris, C.-T. Chen, C.-Y. Mou, C.-S. Yang and L.-W. Lo, “Near-infrared mesoporous silica nanoparticles for optical imaging: characterization and in vivo biodistribution”, Adv. Funct. Mater. 19(2), 215–222 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200800753
E. I. Altinoglu, T. J. Russin, J. M. Kaiser, B. M. Barth, P. C. Eklund, M. Kester and J. H. Adair, “Near-infrared emitting fluorophore-doped calcium phosphate nanoparticles for in vivo imaging of human breast cancer”, Acs Nano 2(10), 2075–2084 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn800448r
K. Sano, T. Nakajima, K. Miyazaki, Y. Ohuchi, T. Ikegami, P. L. Choyke and H. Kobayashi, “Short PEG-linkers improve the performance of targeted, activatable monoclonal antibody-indocyanine green optical imaging probes”, Bioconjug. Chem. 24(5), 811–816 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bc400050k
H. Mok, H. Jeong, S. J. Kim and B. H. Chung, “Indocyanine green encapsulated nanogels for hyaluronidase activatable and selective near infrared imaging of tumors and lymph nodes”, Chem. Commun. (Camb) 48, 8628–8630 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2cc33555g
P. Rungta, Y. P. Bandera, R. D. Roeder, Y. Li, W. S. Baldwin, D. Sharma, M. G. Sehorn, I. Luzinov and S. H. Foulger, “Selective imaging and killing of cancer cells with protein-activated near-infrared fluorescing nanoparticles”, Macromol. Biosci. 11(7), 927–937 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201100043
M. A. Daniele, M. L. Shaughnessy, R. Roeder, A. Childress, Y. P. Bandera and S. Foulger, “Magnetic nanoclusters exhibiting protein-activated near-infrared fluorescence”, Acs Nano 7(1), 203–213 (2013). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/nn3037368