Effects of Reaction Temperature on Microstructure and Advanced Pseudocapacitor Properties of NiO Prepared via Simple Precipitation Method
Corresponding Author: Shujuan Bao
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 5 No. 4 (2013), Article Number: 289-295
Abstract
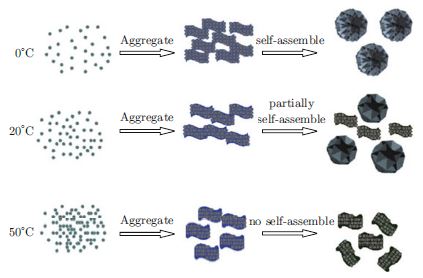
Morphology-controlled synthesis and large-scale self-assembly of nanoscale building blocks into complex nanoarchitectures is still a great challenge in nanoscience. In this work, various porous NiO nanostructures are obtained by a simple ammonia precipitation method and we find that the reaction temperature has a significant impact on their microstructures. Nanoflowers and nanoflakes have been obtained at 0°C and 50°C, while, weakly self-assembly nanoflowers with nanoflakes are formed at 20°C. In order to understand the process-structure-property relationship in nanomaterial synthesis and application, the as-prepared NiO is used as supercapacitor electrode materials, and evaluated by electrochemical measurement. The experimental results indicate that the material obtained at lower temperature has higher pseudocapacitance, the specific capacitance of 944, 889 and 410 F/g are reached for the materials prepared at 0°C, 20°C and 50°C and further calcined at 300°C, respectively. While the material obtained at higher temperature has excellent rate capacity. This offers us an opportunity searching for exciting new properties of NiO, and be useful for fabricating functional nanodevices.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- B. J. Melde and B. J. Johnson, “Mesoporous materials in sensing: morphology and functionality at the meso-interface”, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 398(4), 1565–73 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3688-6
- Q. Li, L.-S. Wang, B.-Y. Hu, C. Yang, L. Zhou and L. Zhang, “Preparation and characterization of NiO nanops through calcination of malate gel”, Mater. Lett. 61(8–9), 1615–1618 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.07.113
- Z.-H. Liang, Y.-J. Zhu and X.-L. Hu, “ß-Nickel hydroxide nanosheets and their thermal decomposition to nickel oxide nanosheets”, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. B 108(11), 3488–3491 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp037513n
- S. A. Needham, G. X. Wang and H. K. Liu, “Synthesis of NiO nanotubes for use as negative electrodes in lithium ion batteries”, J. Power Sources 159(1), 254–257 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.04.025
- C. Xu, K. Hong, S. Liu, G. Wang and X. Zhao, “A novel wet chemical route to NiO nanowires”, J. Cryst. Growth 255(3–4), 308–312 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0022-0248(03)01246-6
- K. Matsui, B. K. Pradhan, T. Kyotani and A. Tomita, “Formation of nickel oxide nanoribbons in the cavity of carbon nanotubes”, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. B 105(24), 5682–5688 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp010496m
- X. Wang, L. Yu, P. Hu and F. Yuan, “Synthesis of single-crystalline hollow octahedral NiO”, Crystal Growth & Design 7(12), 2415–2418 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cg060957z
- B. Varghese, M. Reddy, Z. Yanwu, C. S. Lit, T. C. Hoong, G. Subba Rao, B. Chowdari, A. T. S. Wee, C. T. Lim and C.-H. Sow, “Fabrication of NiO nanowall electrodes for high performance lithium ion battery”, Chem. Mater. 20(10), 3360–3367 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cm703512k
- W. Zhou, M. Yao, L. Guo, Y. Li, J. Li and S. Yang, “Hydrazine-linked convergent self-assembly of sophisticated concave polyhedrons of beta-Ni (OH)2 and NiO from nanoplate building blocks”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(8), 2959–2964 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja808784s
- J. Liu, S. Du, L. Wei, H. Liu, Y. Tian and Y. Chen, “Template-free synthesis of NiO hollow microspheres covered with nanoflakes”, Mater. Lett. 60(29), 3601–3604 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.068
- M.-S. Wu and H.-H. Hsieh, “Nickel oxide/hydroxide nanoplatelets synthesized by chemical precipitation for electrochemical capacitors”, Electrochimica Acta 53(8), 3427–3435 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.005
- Q. Yang, J. Sha, X. Ma and D. Yang, “Synthesis of NiO nanowires by a sol-gel process”, Mater. Lett. 59(14–15), 1967–1970 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.02.037
- P. Palanisamy and A. M. Raichur, “Synthesis of spherical NiO nanops through a novel biosurfactant mediated emulsion technique”, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29(1), 199–204 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.06.008
- E. R. Beach, K. Shqau, S. E. Brown, S. J. Rozeveld and P. A. Morris, “Solvothermal synthesis of crystalline nickel oxide nanops”, Mater. Chem. & Phys. 115(1), 371–377 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.12.018
- Hua Jiao, “Urchin-like NiO Superstructures Prepared by Simple Thermal Decomposition Process”, Nano-Micro Lett. 3(3), 166–170 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v3i3.p166-170
- X. Deng and Z. Chen, “Preparation of nano-NiO by ammonia precipitation and reaction in solution and competitive balance”, Mater. Lett. 58(3), 276–280 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00469-5
- J. Huang, Y. Wu, C. Gu, M. Zhai, K. Yu, M. Yang and J. Liu, “Large-scale synthesis of ?owerlike ZnO nanostructure by a simple chemical solution route and its gas-sensing property”, Sens. Act. B: Chem. 146(1), 206–212 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.052
- L. S. Zhong, J. S. Hu, H. P. Liang, A. M. Cao, W. G. Song and L. J. Wan, “Self-Assembled 3D flowerlike iron oxide nanostructures and their application in water treatment”, Adv. Mater. 18(18), 2426–2431 (2006).http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adma.200600504
- S. Zeng, K. Tang, T. Li, Z. Liang, D. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Qi and W. Zhou, “Facile route for the fabrication of porous hematite nano?owers: its synthesis, growth mechanism, application in the lithium ion battery, and magnetic and photocatalytic properties”, J. Phys.Chem. Lett. C 112(13), 4836–4843 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp0768773
- H. Pang, B. Zhang, J. Du, J. Chen, J. Zhang and S. Li, “Porous nickel oxide nanospindles with huge speci?c capacitance and long-life cycle”, RSC Adv. 2 (6), 2257–2261 (2012).
- B. Chang, X. Zhang, J. Guo, Y. Sun, H. Tang, Q. Ren and W. Yang, “General one-pot strategy to prepare multifunctional nanocomposites with hydrophilic colloidal nanops core/mesoporous silica shell structure”, Journal of colloid and interface science. 377 (1), 64–75 (2012).
References
B. J. Melde and B. J. Johnson, “Mesoporous materials in sensing: morphology and functionality at the meso-interface”, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 398(4), 1565–73 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3688-6
Q. Li, L.-S. Wang, B.-Y. Hu, C. Yang, L. Zhou and L. Zhang, “Preparation and characterization of NiO nanops through calcination of malate gel”, Mater. Lett. 61(8–9), 1615–1618 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.07.113
Z.-H. Liang, Y.-J. Zhu and X.-L. Hu, “ß-Nickel hydroxide nanosheets and their thermal decomposition to nickel oxide nanosheets”, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. B 108(11), 3488–3491 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp037513n
S. A. Needham, G. X. Wang and H. K. Liu, “Synthesis of NiO nanotubes for use as negative electrodes in lithium ion batteries”, J. Power Sources 159(1), 254–257 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.04.025
C. Xu, K. Hong, S. Liu, G. Wang and X. Zhao, “A novel wet chemical route to NiO nanowires”, J. Cryst. Growth 255(3–4), 308–312 (2003). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0022-0248(03)01246-6
K. Matsui, B. K. Pradhan, T. Kyotani and A. Tomita, “Formation of nickel oxide nanoribbons in the cavity of carbon nanotubes”, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. B 105(24), 5682–5688 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp010496m
X. Wang, L. Yu, P. Hu and F. Yuan, “Synthesis of single-crystalline hollow octahedral NiO”, Crystal Growth & Design 7(12), 2415–2418 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cg060957z
B. Varghese, M. Reddy, Z. Yanwu, C. S. Lit, T. C. Hoong, G. Subba Rao, B. Chowdari, A. T. S. Wee, C. T. Lim and C.-H. Sow, “Fabrication of NiO nanowall electrodes for high performance lithium ion battery”, Chem. Mater. 20(10), 3360–3367 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cm703512k
W. Zhou, M. Yao, L. Guo, Y. Li, J. Li and S. Yang, “Hydrazine-linked convergent self-assembly of sophisticated concave polyhedrons of beta-Ni (OH)2 and NiO from nanoplate building blocks”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(8), 2959–2964 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja808784s
J. Liu, S. Du, L. Wei, H. Liu, Y. Tian and Y. Chen, “Template-free synthesis of NiO hollow microspheres covered with nanoflakes”, Mater. Lett. 60(29), 3601–3604 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.068
M.-S. Wu and H.-H. Hsieh, “Nickel oxide/hydroxide nanoplatelets synthesized by chemical precipitation for electrochemical capacitors”, Electrochimica Acta 53(8), 3427–3435 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.12.005
Q. Yang, J. Sha, X. Ma and D. Yang, “Synthesis of NiO nanowires by a sol-gel process”, Mater. Lett. 59(14–15), 1967–1970 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.02.037
P. Palanisamy and A. M. Raichur, “Synthesis of spherical NiO nanops through a novel biosurfactant mediated emulsion technique”, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 29(1), 199–204 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2008.06.008
E. R. Beach, K. Shqau, S. E. Brown, S. J. Rozeveld and P. A. Morris, “Solvothermal synthesis of crystalline nickel oxide nanops”, Mater. Chem. & Phys. 115(1), 371–377 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.12.018
Hua Jiao, “Urchin-like NiO Superstructures Prepared by Simple Thermal Decomposition Process”, Nano-Micro Lett. 3(3), 166–170 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.3786/nml.v3i3.p166-170
X. Deng and Z. Chen, “Preparation of nano-NiO by ammonia precipitation and reaction in solution and competitive balance”, Mater. Lett. 58(3), 276–280 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00469-5
J. Huang, Y. Wu, C. Gu, M. Zhai, K. Yu, M. Yang and J. Liu, “Large-scale synthesis of ?owerlike ZnO nanostructure by a simple chemical solution route and its gas-sensing property”, Sens. Act. B: Chem. 146(1), 206–212 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.02.052
L. S. Zhong, J. S. Hu, H. P. Liang, A. M. Cao, W. G. Song and L. J. Wan, “Self-Assembled 3D flowerlike iron oxide nanostructures and their application in water treatment”, Adv. Mater. 18(18), 2426–2431 (2006).http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/adma.200600504
S. Zeng, K. Tang, T. Li, Z. Liang, D. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Qi and W. Zhou, “Facile route for the fabrication of porous hematite nano?owers: its synthesis, growth mechanism, application in the lithium ion battery, and magnetic and photocatalytic properties”, J. Phys.Chem. Lett. C 112(13), 4836–4843 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp0768773
H. Pang, B. Zhang, J. Du, J. Chen, J. Zhang and S. Li, “Porous nickel oxide nanospindles with huge speci?c capacitance and long-life cycle”, RSC Adv. 2 (6), 2257–2261 (2012).
B. Chang, X. Zhang, J. Guo, Y. Sun, H. Tang, Q. Ren and W. Yang, “General one-pot strategy to prepare multifunctional nanocomposites with hydrophilic colloidal nanops core/mesoporous silica shell structure”, Journal of colloid and interface science. 377 (1), 64–75 (2012).