Structure and Magnetic Properties of Monodisperse Fe3+-doped CeO2 Nanospheres
Corresponding Author: Santi Maensiri
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 5 No. 4 (2013), Article Number: 223-233
Abstract
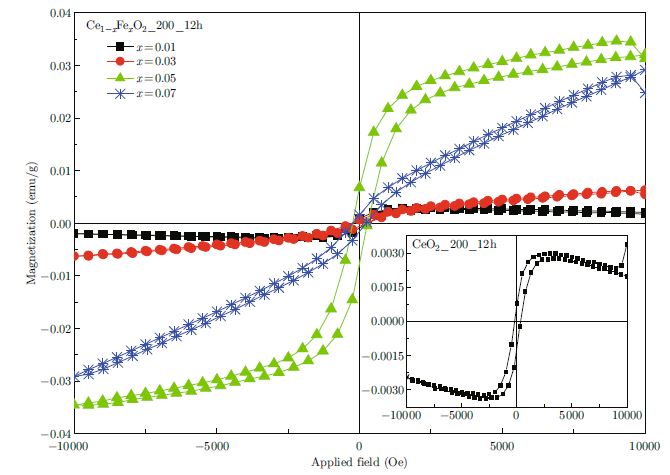
This work reports the study concerning the structure and magnetic properties of undoped CeO2 and Fe-doped CeO2 (Ce1−xFe x O2, 0.01 ≤ x ≤ 0.07) nanospheres with diameters of 100∼200 nm prepared by hydrothermal method using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as surfactant. The prepared samples were studied by using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES), and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). The XRD results showed that Fe-doped CeO2 was single-phased with a cubic structure, and with Fe3+ successfully substituting in Ce4+ sites. Raman spectra showed a redshift of F2g mode that caused by the Fe doping. The samples of both undoped CeO2 and Fe-doped CeO2 exhibited room temperature ferromagnetism, and the saturated magnetization (M s ) increased with increasing Fe content until x = 0.05, and then the samples displayed ferromagnetic loops as well as paramagnetic behavior. The roles of Ce3+ and Fe3+ spin electrons are discussed for the ferromagnetism in the Fe-doped CeO2.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert and D. Ferrand, “Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors”, Science 287(5455), 1019–1022 (2000). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5455.1019
- S. J. Pearton, W. H. Heo, M. Ivill, D. P. Norton and T. Steiner, “Dilute magnetic semiconducting oxides”, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 19(10), R59 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/19/10/R01
- N. H. Hong, J. Sakai, N. Poirot and V. Brize, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films”, Phys. Rev. B 73 (13), 132404 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.132404
- X. Chen, G. Li, Y. Su, X. Qui, L. Li and Z. Zou, “Synthesis and room-temperature ferromagnetism of CeO2 nanocrystals with nonmagnetic Ca2+ doping”, Nanotechnology 20(11), 115606 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/11/115606
- A. Tiwari, V. M. Bhosle, S. Ramachandran, N. Sudhakar, J. Narayan, S. Budak and A. Gupta, “Ferromagnetism in Co doped CeO2: Observation of a giant magnetic moment with a high Curie temperature”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(14), 142511 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2193431
- Y. Q. Song, H. W. Zhang, Q. Y. Wen, Y. X. Li and J. Q. Xiao, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism of co-doped CeO2 thin films on si(111) substrates”, Chin. Phys. Lett. 24(1), 218–221 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/24/1/059
- B. Vodungbo, Y. Zheng, F. Vidal, D. Demaille, V. H. Etgens and D. H. Mosca, “Room temperature ferromagnetism of Co doped CeO2−δ diluted magnetic oxide: Effect of oxygen and anisotropy”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(6), 062510 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2472520
- V. Fernandes, J. J. Klein, N. Mattoso, D. H. Mosca, E. Silveira, E. Ribeiro, W. H. Schreiner, J. Varalda and A. J. A. de Oliveira, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped CeO2 films on Si(001)”, Phys. Rev. B 75(12), 121304R (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.121304
- A. Thurber, K. M. Reddy, V. Shutthanandan, M. H. Engelhard, C. Wang, J. Hays and Punnoose, “Ferromagnetism in chemically synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles by Ni doping”, Phys. Rev. B 76(16), 165206 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.165206
- Q. Y. Wen, H. W. Zhang, Y. Q. Song, Q. H. Yang, H. Zhu and J. Q. Xiao, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism in pure and Co doped CeO2 powders”, J. Phys.: Condens. Mat. 19(24), 246205 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/24/246205
- Y. N. Ou, G. R. Li, J. H. Liang, Z. P. Feng and Y. X. Tong, “Ce1−xCoxO2−δ nanorods grown by electrochemical deposition and their magnetic properties”, J. Phys. Chem. C 114(32), 13509–13514 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp1038128
- P. C. A. Brito, D. A. A. Santos, J. G. S. Duque and M. A. M. Macedo, “Structural and magnetic study of Fe-doped CeO2”, Physica B 405(7), 1821–1825 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.01.054
- M. Y. Ge, H. Wang, E. Z. Liu, J. F. Liu, J. Z. Jiang, Y. K. Li, Z. A. Xu and H. Y. Li, “On the origin of ferromagnetism in CeO2 nanocubes”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 062505 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2972118
- S. Kumar, Y. J. Kim, B. H. Koo, and C. G. Lee and J. Nanosci. “Structural and magnetic properties of Ni doped CeO2 nanoparticles”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10(11), 7204–7207 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2010.2751
- P. O. Maksimchuk, A. A. Masalov, Yu.V. Malyukin, “Spectroscopically detected formation of oxygen vacancies in nano-crystalline CeO2−x”, J. Nano-Electron. Phys. 5(1), 01004 (2013).
- S. Maensiri, S. Phokha, P. Laokul, and S. Seraphin, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped CeO2 nanoparticles”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9(11), 6415–6420 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.1372
- S. Phokha, S. Pinitsoontorn, P. Chirawatkul, Y. Poo-arporn and S. Maensiri, “Synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of monodisperse CeO2 nanospheres prepared by PVP-assisted hydrothermal method”, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 425 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-425
- M. C. Dimri, H. Khanduri, H. Kooskora, J. Subbi, I. Heinmaa, A. Mere, J. Krustok and R. Stern, “Ferromagnetism in rare earth doped cerium oxide bulk samples”, Phys. Status Solidi A 209(2), 353–358 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201127403
- N. Paunović, Z. D. Mitrović, R. Scurtu, S. Aškrabić, M. Prekajski, B. Matović and Z. V. Popović, “Suppression of inherent ferromagnetism in Pr-doped CeO2 nanocrystals”, Nanoscale, 4 (17), 5469–5476 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2nr30799e
- K. Ackland, L. M. A. Monzon, M. Venkatesan and J. M. D. Coey, “Magnetism of Nanostructured CeO2”, IEEE Trans. Magn. 47(10), 3509–3512 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2150743
- A. Sundaresan, R. Bhargavi, N. Rangarajan, U. Siddesh and C. N. R. Rao, “Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides”, Phys. Rev. B 74 (16), 161306 (R) (2006).
- S. Maensiri, C. Marsingboon, P. Loakul, W. Jareonboon, V. Promarak, P. L. Anderson and S. Seraphin, “Egg white synthesis and photoluminescence of platelike clusters of CeO2 nanoparticles”, Cryst. Growth. Des. 7(5), 950–955 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cg0608864
- S. Phoka, P. Laokul, E. Swatsitang, V. Promarak, S. Seraphinc and S. Maensiri, “Synthesis, structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a simple polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) solution route”, Mater. Chem. Phys. 115(1), 423–428 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.12.031
- I. Kosacki, T. Suzuki, V. Petrovsky, H. U. Anderson and Ph. Colomban, “Raman scattering and lattice defects in nanocrystalline CeO2 thin films”, Solid State Ionics 149(1–2), 99–105 (2002).
- I. Kosacki, V. Petrovsky, H. U. Anderson and Ph. Colomban, “Raman spectroscopy of nanocrystalline ceria and zirconia thin films”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85(11), 2646–2650 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2002.tb00509.x
- Z. D. Dohcevic-Mitrovic, N. Paunovic, M. Radovic, Z. V. Popovic, B. Matovic, B. Cekic and V. Ivanovski, “Valence state dependent room-temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ceria nanocrystals”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96(20), 203104 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3431581
- F. Zhou, X. Ni, Y. Zhang and H. Zheng, “Size-controlled synthesis and electrochemical characterization of spherical CeO2 crystallites”, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 307(1), 135–138 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.11.005
- L. Wen, B. Liu, X. Zhao, K. Nakata, T. Murakami and A. Fujishima, “Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of Fe-doped TiO2: A combined experimental and theoretical study”, Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 368750 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/368750
- J. Hormes, M. Pantelouris, G.B. Balazs and B. Rambabu, “X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) measurements of ceria-based solid electrolytes”, Solid State Ionics 136–137, 945–954 (2000). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00533-6
- F. Zhang, P. Wang, J. Koberstein, S. Khalid and S. W. Chan, “Cerium oxidation state in ceria nanoparticles studied with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and absorption near edge spectroscopy”, Surf. Sci. 563(1-3), 78–82 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2004.05.138
- J. Zhang, Z. Wu, T. Liu, T. Hu, Z. Wu and X. Ju, “XANES study on the valence transitions in cerium oxide nanoparticles”, J. Synchrotron Radiat. 8, 531–532 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0909049500016022
- C. Wan, X. Ju, Y. Qi, Y. Zhang, S. Wang. X. Liu and L. Jiang, “Synchrotron XRD and XANES studies of cerium-doped NaAlH4: Elucidation of doping induced structure changes and electronic state”, J. Alloy. Compd. 481(1–2), 60–64 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.128
- J. Wang, B. Zhang, M. Shen, J. Wang, W. Wang, J. Ma, S. Liu and L. Jia, “Effects of Fe-doping of ceriabased materials on their microstructural and dynamic oxygen storage and release properties”, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 58(1), 259–268 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2386-3
- A. Ohta, H. Tsuno, H. Kagi, Y. Kanai, M. Nomura, R. Zhang, S. Terashima and N. Imai, “Chemical compositions and XANES speciations of Fe, Mn and Zn from aerosols collected in China and Japan during dust events”, Geochem. J. 40(4), 363–376 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.40.363
- R. K. Singhal, P. Kumari, S. Kumar, S. N. Dolia, Y. T. Xing, M. Alzamora, U. P. Deshpande, T. Shripathi and E. Saitovitch, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in pure and Co- and Fe-doped CeO2 dilute magnetic oxide: Effect of oxygen vacancies and cation valence”, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44(16), 165002 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/16/165002
- S. Maensiri, S. Phokha, P. Laokul and S. Seraphin, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-Doped CeO2 nanoparticles”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnology 9(11), 6415–6420 (2009).
- J. M. D. Coey, M. Venkatesan and C. B. Fitzerald, “Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides”, Nat. Mater. 4(2), 173–179 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmat1310
- V. Fernandes, R. J. O. Mossanek, P. Schio, J. J. Klein, A. J. A. de Oliveira, W. A. Ortiz, N. Mattoso, J. Varalda, W. H. Schreiner, M. Abbate and D. H. Mosca, “Dilute-defect magnetism: Origin of magnetism in nanocrystalline CeO2”, Phys. Rev. B 80 (3), 035202 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.035202
- J. M. D. Coey, A. P. Douvalis, C. B. Fitzgerald and M. Venkatesan, “Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(8), 1332–1334 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1650041
- F. Esch, S. Fabris, L. Zhou, T. Montini, C. Africh, P. Fornasiero, G. Comelli and R. Rosei, “Electron localization determines defect formation on ceria substrates”, Science, 309(5735), 752–755 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1111568
- M. Radovic, Z. Dohcevic-Mitrovic, N. Paunovic, M. Scepanovic, B. Matovic and Z. V. Popovic, “Hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2 and Ce0.9Fe0.1O2 nanocrystals”, Acta Phys. Pol. A 116(4), 614–617 (2009).
- V. Fernandes, P. Schio, A. J. A. de. Oliveira, W. H. Schreiner, and J. Varalda and D. H. Mosca, “Loss of magnetization induced by doping in CeO2 films”, J. Appl. Phys. 110(11), 113902 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3664764
- S. Colis, A. Bouaine, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, A. Dinia, S. Choua and P. Turek, “High-temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped CeO2 synthesized by the coprecipitation technique”, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(20), 7256–7263 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2cp23973f
References
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert and D. Ferrand, “Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors”, Science 287(5455), 1019–1022 (2000). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.287.5455.1019
S. J. Pearton, W. H. Heo, M. Ivill, D. P. Norton and T. Steiner, “Dilute magnetic semiconducting oxides”, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 19(10), R59 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/19/10/R01
N. H. Hong, J. Sakai, N. Poirot and V. Brize, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films”, Phys. Rev. B 73 (13), 132404 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.73.132404
X. Chen, G. Li, Y. Su, X. Qui, L. Li and Z. Zou, “Synthesis and room-temperature ferromagnetism of CeO2 nanocrystals with nonmagnetic Ca2+ doping”, Nanotechnology 20(11), 115606 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/11/115606
A. Tiwari, V. M. Bhosle, S. Ramachandran, N. Sudhakar, J. Narayan, S. Budak and A. Gupta, “Ferromagnetism in Co doped CeO2: Observation of a giant magnetic moment with a high Curie temperature”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88(14), 142511 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2193431
Y. Q. Song, H. W. Zhang, Q. Y. Wen, Y. X. Li and J. Q. Xiao, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism of co-doped CeO2 thin films on si(111) substrates”, Chin. Phys. Lett. 24(1), 218–221 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/24/1/059
B. Vodungbo, Y. Zheng, F. Vidal, D. Demaille, V. H. Etgens and D. H. Mosca, “Room temperature ferromagnetism of Co doped CeO2−δ diluted magnetic oxide: Effect of oxygen and anisotropy”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(6), 062510 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2472520
V. Fernandes, J. J. Klein, N. Mattoso, D. H. Mosca, E. Silveira, E. Ribeiro, W. H. Schreiner, J. Varalda and A. J. A. de Oliveira, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped CeO2 films on Si(001)”, Phys. Rev. B 75(12), 121304R (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.75.121304
A. Thurber, K. M. Reddy, V. Shutthanandan, M. H. Engelhard, C. Wang, J. Hays and Punnoose, “Ferromagnetism in chemically synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles by Ni doping”, Phys. Rev. B 76(16), 165206 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.76.165206
Q. Y. Wen, H. W. Zhang, Y. Q. Song, Q. H. Yang, H. Zhu and J. Q. Xiao, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism in pure and Co doped CeO2 powders”, J. Phys.: Condens. Mat. 19(24), 246205 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/24/246205
Y. N. Ou, G. R. Li, J. H. Liang, Z. P. Feng and Y. X. Tong, “Ce1−xCoxO2−δ nanorods grown by electrochemical deposition and their magnetic properties”, J. Phys. Chem. C 114(32), 13509–13514 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp1038128
P. C. A. Brito, D. A. A. Santos, J. G. S. Duque and M. A. M. Macedo, “Structural and magnetic study of Fe-doped CeO2”, Physica B 405(7), 1821–1825 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.01.054
M. Y. Ge, H. Wang, E. Z. Liu, J. F. Liu, J. Z. Jiang, Y. K. Li, Z. A. Xu and H. Y. Li, “On the origin of ferromagnetism in CeO2 nanocubes”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 062505 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2972118
S. Kumar, Y. J. Kim, B. H. Koo, and C. G. Lee and J. Nanosci. “Structural and magnetic properties of Ni doped CeO2 nanoparticles”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10(11), 7204–7207 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2010.2751
P. O. Maksimchuk, A. A. Masalov, Yu.V. Malyukin, “Spectroscopically detected formation of oxygen vacancies in nano-crystalline CeO2−x”, J. Nano-Electron. Phys. 5(1), 01004 (2013).
S. Maensiri, S. Phokha, P. Laokul, and S. Seraphin, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped CeO2 nanoparticles”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9(11), 6415–6420 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2009.1372
S. Phokha, S. Pinitsoontorn, P. Chirawatkul, Y. Poo-arporn and S. Maensiri, “Synthesis, characterization, and magnetic properties of monodisperse CeO2 nanospheres prepared by PVP-assisted hydrothermal method”, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 425 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-425
M. C. Dimri, H. Khanduri, H. Kooskora, J. Subbi, I. Heinmaa, A. Mere, J. Krustok and R. Stern, “Ferromagnetism in rare earth doped cerium oxide bulk samples”, Phys. Status Solidi A 209(2), 353–358 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201127403
N. Paunović, Z. D. Mitrović, R. Scurtu, S. Aškrabić, M. Prekajski, B. Matović and Z. V. Popović, “Suppression of inherent ferromagnetism in Pr-doped CeO2 nanocrystals”, Nanoscale, 4 (17), 5469–5476 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2nr30799e
K. Ackland, L. M. A. Monzon, M. Venkatesan and J. M. D. Coey, “Magnetism of Nanostructured CeO2”, IEEE Trans. Magn. 47(10), 3509–3512 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2150743
A. Sundaresan, R. Bhargavi, N. Rangarajan, U. Siddesh and C. N. R. Rao, “Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides”, Phys. Rev. B 74 (16), 161306 (R) (2006).
S. Maensiri, C. Marsingboon, P. Loakul, W. Jareonboon, V. Promarak, P. L. Anderson and S. Seraphin, “Egg white synthesis and photoluminescence of platelike clusters of CeO2 nanoparticles”, Cryst. Growth. Des. 7(5), 950–955 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cg0608864
S. Phoka, P. Laokul, E. Swatsitang, V. Promarak, S. Seraphinc and S. Maensiri, “Synthesis, structural and optical properties of CeO2 nanoparticles synthesized by a simple polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) solution route”, Mater. Chem. Phys. 115(1), 423–428 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.12.031
I. Kosacki, T. Suzuki, V. Petrovsky, H. U. Anderson and Ph. Colomban, “Raman scattering and lattice defects in nanocrystalline CeO2 thin films”, Solid State Ionics 149(1–2), 99–105 (2002).
I. Kosacki, V. Petrovsky, H. U. Anderson and Ph. Colomban, “Raman spectroscopy of nanocrystalline ceria and zirconia thin films”, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85(11), 2646–2650 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.2002.tb00509.x
Z. D. Dohcevic-Mitrovic, N. Paunovic, M. Radovic, Z. V. Popovic, B. Matovic, B. Cekic and V. Ivanovski, “Valence state dependent room-temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ceria nanocrystals”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96(20), 203104 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3431581
F. Zhou, X. Ni, Y. Zhang and H. Zheng, “Size-controlled synthesis and electrochemical characterization of spherical CeO2 crystallites”, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 307(1), 135–138 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2006.11.005
L. Wen, B. Liu, X. Zhao, K. Nakata, T. Murakami and A. Fujishima, “Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of Fe-doped TiO2: A combined experimental and theoretical study”, Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 368750 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/368750
J. Hormes, M. Pantelouris, G.B. Balazs and B. Rambabu, “X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) measurements of ceria-based solid electrolytes”, Solid State Ionics 136–137, 945–954 (2000). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00533-6
F. Zhang, P. Wang, J. Koberstein, S. Khalid and S. W. Chan, “Cerium oxidation state in ceria nanoparticles studied with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and absorption near edge spectroscopy”, Surf. Sci. 563(1-3), 78–82 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.susc.2004.05.138
J. Zhang, Z. Wu, T. Liu, T. Hu, Z. Wu and X. Ju, “XANES study on the valence transitions in cerium oxide nanoparticles”, J. Synchrotron Radiat. 8, 531–532 (2001). http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S0909049500016022
C. Wan, X. Ju, Y. Qi, Y. Zhang, S. Wang. X. Liu and L. Jiang, “Synchrotron XRD and XANES studies of cerium-doped NaAlH4: Elucidation of doping induced structure changes and electronic state”, J. Alloy. Compd. 481(1–2), 60–64 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.128
J. Wang, B. Zhang, M. Shen, J. Wang, W. Wang, J. Ma, S. Liu and L. Jia, “Effects of Fe-doping of ceriabased materials on their microstructural and dynamic oxygen storage and release properties”, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 58(1), 259–268 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10971-010-2386-3
A. Ohta, H. Tsuno, H. Kagi, Y. Kanai, M. Nomura, R. Zhang, S. Terashima and N. Imai, “Chemical compositions and XANES speciations of Fe, Mn and Zn from aerosols collected in China and Japan during dust events”, Geochem. J. 40(4), 363–376 (2006). http://dx.doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.40.363
R. K. Singhal, P. Kumari, S. Kumar, S. N. Dolia, Y. T. Xing, M. Alzamora, U. P. Deshpande, T. Shripathi and E. Saitovitch, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in pure and Co- and Fe-doped CeO2 dilute magnetic oxide: Effect of oxygen vacancies and cation valence”, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44(16), 165002 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/44/16/165002
S. Maensiri, S. Phokha, P. Laokul and S. Seraphin, “Room temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-Doped CeO2 nanoparticles”, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnology 9(11), 6415–6420 (2009).
J. M. D. Coey, M. Venkatesan and C. B. Fitzerald, “Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides”, Nat. Mater. 4(2), 173–179 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmat1310
V. Fernandes, R. J. O. Mossanek, P. Schio, J. J. Klein, A. J. A. de Oliveira, W. A. Ortiz, N. Mattoso, J. Varalda, W. H. Schreiner, M. Abbate and D. H. Mosca, “Dilute-defect magnetism: Origin of magnetism in nanocrystalline CeO2”, Phys. Rev. B 80 (3), 035202 (2009). http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.035202
J. M. D. Coey, A. P. Douvalis, C. B. Fitzgerald and M. Venkatesan, “Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(8), 1332–1334 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1650041
F. Esch, S. Fabris, L. Zhou, T. Montini, C. Africh, P. Fornasiero, G. Comelli and R. Rosei, “Electron localization determines defect formation on ceria substrates”, Science, 309(5735), 752–755 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1111568
M. Radovic, Z. Dohcevic-Mitrovic, N. Paunovic, M. Scepanovic, B. Matovic and Z. V. Popovic, “Hydrothermal synthesis of CeO2 and Ce0.9Fe0.1O2 nanocrystals”, Acta Phys. Pol. A 116(4), 614–617 (2009).
V. Fernandes, P. Schio, A. J. A. de. Oliveira, W. H. Schreiner, and J. Varalda and D. H. Mosca, “Loss of magnetization induced by doping in CeO2 films”, J. Appl. Phys. 110(11), 113902 (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3664764
S. Colis, A. Bouaine, G. Schmerber, C. Ulhaq-Bouillet, A. Dinia, S. Choua and P. Turek, “High-temperature ferromagnetism in Co-doped CeO2 synthesized by the coprecipitation technique”, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(20), 7256–7263 (2012). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/c2cp23973f