Effects of Magnetic Particles Entrance Arrangements on Mixing Efficiency of a Magnetic Bead Micromixer
Corresponding Author: Reza Kamali
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 6 No. 1 (2014), Article Number: 30-37
Abstract
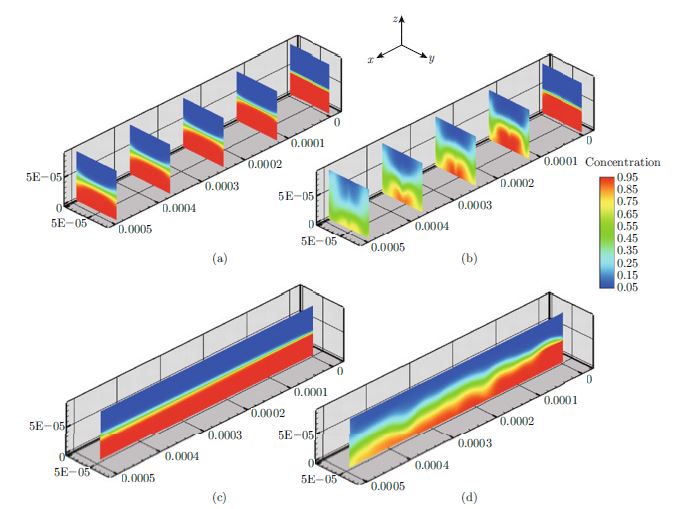
In this study, a computer code is developed to numerically investigate a magnetic bead micromixer under different conditions. The micromixer consists of a microchannel and numerous micro magnetic particles which enter the micromixer by fluid flows and are actuated by an alternating magnetic field normal to the main flow. An important feature of micromixer which is not considered before by researchers is the particle entrance arrangement into the micromixer. This parameter could effectively affect the micromixer efficiency. There are two general micro magnetic particle entrance arrangements in magnetic bead micromixers: determined position entrance and random position entrance. In the case of determined position entrances, micro magnetic particles enter the micromixer at specific positions of entrance cross section. However, in a random position entrance, particles enter the microchannel with no order. In this study mixing efficiencies of identical magnetic bead micromixers which only differ in particle entrance arrangement are numerically investigated and compared. The results reported in this paper illustrate that the prepared computer code can be one of the most powerful and beneficial tools for the magnetic bead micromixer performance analysis. In addition, the results show that some features of the magnetic bead micromixer are strongly affected by the entrance arrangement of the particles.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- J. Yue, G. Chen and Q. Yuan “Pressure drops of single and two-phase flows through T-type microchannel mixers”, Chem. Eng. 102(1), 11–24 (2004). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894704000518
- C. Li and T. Chen, “Simulation and optimization of chaotic micromixer using lattice Boltzmann method”, Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 106(2), 871–877 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.09.006
- E. A. Mansur, M. Ye, Y. Wang and Y. Dai, “AState-of-the-Artreview of mixing in microfluidic mixers”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 16(4), 503–516 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(08)60114-7
- M. Zolgharni, S. M. Azimi, M. R. Bahmanyar and W. Balachandran, “A numerical design study of chaotic mixing of magnetic particles in a microfluidic bio-separator”, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 3(6), 677–687 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0160-9
- Y. Wang, J. Zhe and B. T. F. Chung, “A rapid magnetic particle driven micromixer”, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 4(5), 375–389 2008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0188-x
- V. Hessel, H. Lowe and F. Schonfeld, “Micromixers— a review on passive and active mixing principles”, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60(8–9), 2479–2501 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.11.033
- T. N. Le, Y. K. Suh and S. Kang, “A numerical study on flow and mixing in a microchannel using magnetic particles”, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 24(1), 441–450 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-1107-8
- H. Suzuki and C. M. Ho, “A magnetic force driven chaotic micro-mixer”, Proceedings of Micro Electromechanical Systems (MEMS), 40–43 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MEMSYS.2002.984076
- R. Rong, J. W. Choi and C. H. Ahn, “A novel magnetic chaotic mixer for in-flow mixing of magnetic beads”, Proceedingsof International conference on miniaturized chemical and biochemical analysis systems (2003).
- A. Rida and M. A. M. Gijs, “Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying”, Anal. Chem. 76(21), 6239–6246 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ac049415j
- M. F. Lai and C. P. Lee, “Microseparator for magnetic particle separations”, J. Appl. Phys. 107(9), 1–4 2010. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3358615
- H. Suzuki and C. M. Ho, “A chaotic mixer for magnetic bead-based micro cell sorter”, J.Microelectromech. Syst. 13(5), 779–789 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2004.835775
- M. Grumann, A. Geipel, L. Riegger, R. Zengerle and J. Ducrée, “Batch-mode mixing on centrifugal microfluidic platforms”, Lab Chip 5, 560–565 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b418253g
- Y. D. Sobral, T. F. Oliveira and F. R. Cunha, “On the unsteady forces during the motion of a sedimenting particle”, Powder Technol. 178(2), 129–141 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2007.04.012
- A. Prosperetti and G. Tryggvason, “Computational methods for multiphase flow”, Cambridge University Press (2007).Book DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511607486
- S. V. Patankar, “Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow”, Hemisphere Publish Corporation (1980).
- C. Crowe, M. Sommerfield and Y. Tsuji, “Multiphase flows with droplets and particles”, CRC Press (1998).
- F. M. White, “Viscous Fluid Flow”, McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, 2nd edition (1991).
References
J. Yue, G. Chen and Q. Yuan “Pressure drops of single and two-phase flows through T-type microchannel mixers”, Chem. Eng. 102(1), 11–24 (2004). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894704000518
C. Li and T. Chen, “Simulation and optimization of chaotic micromixer using lattice Boltzmann method”, Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 106(2), 871–877 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2004.09.006
E. A. Mansur, M. Ye, Y. Wang and Y. Dai, “AState-of-the-Artreview of mixing in microfluidic mixers”, Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 16(4), 503–516 (2008). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1004-9541(08)60114-7
M. Zolgharni, S. M. Azimi, M. R. Bahmanyar and W. Balachandran, “A numerical design study of chaotic mixing of magnetic particles in a microfluidic bio-separator”, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 3(6), 677–687 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0160-9
Y. Wang, J. Zhe and B. T. F. Chung, “A rapid magnetic particle driven micromixer”, Microfluid. Nanofluid. 4(5), 375–389 2008. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0188-x
V. Hessel, H. Lowe and F. Schonfeld, “Micromixers— a review on passive and active mixing principles”, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60(8–9), 2479–2501 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2004.11.033
T. N. Le, Y. K. Suh and S. Kang, “A numerical study on flow and mixing in a microchannel using magnetic particles”, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 24(1), 441–450 (2010). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-1107-8
H. Suzuki and C. M. Ho, “A magnetic force driven chaotic micro-mixer”, Proceedings of Micro Electromechanical Systems (MEMS), 40–43 (2002). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MEMSYS.2002.984076
R. Rong, J. W. Choi and C. H. Ahn, “A novel magnetic chaotic mixer for in-flow mixing of magnetic beads”, Proceedingsof International conference on miniaturized chemical and biochemical analysis systems (2003).
A. Rida and M. A. M. Gijs, “Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying”, Anal. Chem. 76(21), 6239–6246 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ac049415j
M. F. Lai and C. P. Lee, “Microseparator for magnetic particle separations”, J. Appl. Phys. 107(9), 1–4 2010. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3358615
H. Suzuki and C. M. Ho, “A chaotic mixer for magnetic bead-based micro cell sorter”, J.Microelectromech. Syst. 13(5), 779–789 (2004). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2004.835775
M. Grumann, A. Geipel, L. Riegger, R. Zengerle and J. Ducrée, “Batch-mode mixing on centrifugal microfluidic platforms”, Lab Chip 5, 560–565 (2005). http://dx.doi.org/10.1039/b418253g
Y. D. Sobral, T. F. Oliveira and F. R. Cunha, “On the unsteady forces during the motion of a sedimenting particle”, Powder Technol. 178(2), 129–141 (2007). http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2007.04.012
A. Prosperetti and G. Tryggvason, “Computational methods for multiphase flow”, Cambridge University Press (2007).Book DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511607486
S. V. Patankar, “Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow”, Hemisphere Publish Corporation (1980).
C. Crowe, M. Sommerfield and Y. Tsuji, “Multiphase flows with droplets and particles”, CRC Press (1998).
F. M. White, “Viscous Fluid Flow”, McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, 2nd edition (1991).