Low-Programmable-Voltage Nonvolatile Memory Devices Based on Omega-shaped Gate Organic Ferroelectric P(VDF-TrFE) Field Effect Transistors Using p-type Silicon Nanowire Channels
Corresponding Author: Dae Joon Kang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 7 No. 1 (2015), Article Number: 35-41
Abstract
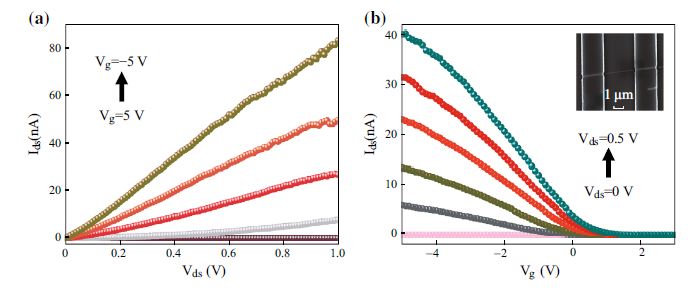
A facile approach was demonstrated for fabricating high-performance nonvolatile memory devices based on ferroelectric-gate field effect transistors using a p-type Si nanowire coated with omega-shaped gate organic ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) (P(VDF-TrFE)). We overcame the interfacial layer problem by incorporating P(VDF-TrFE) as a ferroelectric gate using a low-temperature fabrication process. Our memory devices exhibited excellent memory characteristics with a low programming voltage of ±5 V, a large modulation in channel conductance between ON and OFF states exceeding 105, a long retention time greater than 3 × 104 s, and a high endurance of over 105 programming cycles while maintaining an ION/IOFF ratio higher than 102.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- T.P. Ma, J.P. Han, Why is nonvolatile ferroelectric memory field-effect transistor still elusive? IEEE. Electron. Device Lett. 23(7), 386–388 (2002). doi:10.1109/LED.2002.1015207
- H. Ishiwara, Current status, Prospects of FET-type ferroelectric memories. Annual Device Research Conference Digest 6-9(1999). doi:10.1109/DRC.1999.806306
- J. Hoffman, X. Pan, J.W. Reiner, F.J. Walker, J.P. Han, C.H. Ahn, T.P. Ma, Ferroelectric field effect transistors for memory applications. Adv. Mater. 22(26–27), 2957–2961 (2010). doi:10.1002/adma.200904327
- M. Tang, X. Xu, Z. Ye, Y. Sugiyama, H. Ishiwara, Impact of HfTaO buffer layer on data retention characteristics of ferroelectric-gate FET for nonvolatile memory applications. IEEE. Trans. Electron. Device 58(2), 370–375 (2011). doi:10.1109/TED.2010.2090883
- L. Liao, H.J. Fan, B. Yan, Z. Zhang, L.L. Chen, B.S. Li, G.Z. Xing, Z.X. Shen, T. Wu, X.W. Sun, J. Wang, T. Yu, Ferroelectric transistors with nanowire channel: toward nonvolatile memory applications. ACS Nano 3(3), 700–706 (2009). doi:10.1021/nn800808s
- J. Appenzeller, J. Knoch, M.T. Björk, H. Riel, H. Schmid, W. Riess, Toward nanowire electronics. IEEE. Trans. Electron. Device 55(11), 2827–2845 (2008). doi:10.1109/TED.2008.2008011
- J. Xiang, W. Lu, Y. Hu, Y. Wu, H. Yan, C.M. Lieber, Ge/Si nanowire heterostructures as high-performance field-effect transistors. Nature 441(7092), 489–493 (2006). doi:10.1038/nature04796
- Y. Cui, Z. Zhong, D. Wang, W.U. Wang, C.M. Lieber, High performance silicon nanowire field effect transistors. Nano Lett. 3(2), 149–152 (2003). doi:10.1021/nl025875l
- J.Y. Son, S. Ryu, Y.C. Park, Y.T. Lim, Y.S. Shin, Y.H. Shin, H.M. Jang, A nonvolatile memory device made of a ferroelectric polymer gate nanodot and a single-walled carbon nanotube. ACS Nano 4(12), 7315–7320 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn1021296
- Y. Zheng, G.X. Ni, C.T. Toh, C.Y. Tan, K. Yao, B. Özyilmaz, Graphene field-effect transistors with ferroelectric gating. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(16), 166602–166604 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.166602
- T.W. Koo, D.S. Kim, J.H. Lee, Y.C. Jung, J.W. Lee, Y.S. Yu, S.W. Hwang, D. Whang, Axial p-n nanowire gated diodes as a direct probe of surface-dominated charge dynamics in semiconductor nanomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(47), 23552–23557 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp206639b
- S. Cha, S.M. Kim, H. Kim, J. Ku, J.I. Sohn, Y.J. Park, B.G. Song, M.H. Jung, E.K. Lee, B.L. Choi, J.J. Park, Z.L. Wang, J.M. Kim, K. Kim, Porous PVDF as effective sonic wave driven nanogenerators. Nano Lett. 11(12), 5142–5147 (2011). doi:10.1021/nl202208n
- O. Hayden, M.T. Björk, H. Schmid, H. Riel, U. Drechsler, S.F. Karg, E. Lörtscher, W. Riess, Fully depleted nanowire field-effect transistor in inversion mode. Small 3(2), 230–234 (2007). doi:10.1002/smll.200600325
- W.W. Fang, N. Singh, K.L. Bera, H.S. Nguyen, S.C. Rustagi, G.Q. Lo, N. Balasubramanian, D.L. Kwong, Vertically stacked sige nanowire array channel cmos transistors. IEEE. Electron. Device Lett. 28(3), 211–213 (2007). doi:10.1109/LED.2007.891268
- J.I. Sohn, S.S. Choi, S.M. Morris, J.S. Bendall, H.J. Coles, W.K. Hong, G. Jo, T. Lee, M.E. Welland, Novel nonvolatile memory with multibit storage based on a ZnO nanowire transistor. Nano Lett. 10(11), 4316–4320 (2010). doi:10.1021/nl1013713
- S. Das, J. Appenzeller, FETRAM. An organic ferroelectric material based novel random access memory cell. Nano Lett. 11(9), 4003–4007 (2011). doi:10.1021/nl2023993
- Y.T. Lee, P.J. Jeon, K.H. Lee, R. Ha, H.J. Choi, S. Im, Ferroelectric nonvolatile nanowire memory circuit using a single ZnO nanowire and copolymer top layer. Adv. Mater. 24(22), 3020–3025 (2012). doi:10.1002/adma.201201051
- N.H. Van, J.H. Lee, J.I. Sohn, S.N. Cha, D. Whang, J.M. Kim, D.J. Kang, High performance Si nanowire field-effect-transistors based on a CMOS inverter with tunable threshold voltage. Nanoscale 6(10), 5479–5483 (2014). doi:10.1039/c3nr06690h
- L.B. Luo, X.B. Yang, F.X. Liang, H. Xu, Y. Zhao, X. Xie, W.F. Zhang, S.T. Lee, Surface defects-induced p-type conduction of silicon nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(38), 18453–18458 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp205171j
- K. Keem, D.Y. Jeong, S. Kim, M.S. Lee, I.S. Yeo, U.I. Chung, J.T. Moon, Fabrication and device characterization of omega-shaped-gate ZnO nanowire field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 6(7), 1454–1458 (2006). doi:10.1021/nl060708x
- H. Ishiwara, Current status of ferroelectric-gate Si transistors and challenge to ferroelectric-gate CNT transistors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(1 Suppl.), S2–S6 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.cap.2008.02.013
References
T.P. Ma, J.P. Han, Why is nonvolatile ferroelectric memory field-effect transistor still elusive? IEEE. Electron. Device Lett. 23(7), 386–388 (2002). doi:10.1109/LED.2002.1015207
H. Ishiwara, Current status, Prospects of FET-type ferroelectric memories. Annual Device Research Conference Digest 6-9(1999). doi:10.1109/DRC.1999.806306
J. Hoffman, X. Pan, J.W. Reiner, F.J. Walker, J.P. Han, C.H. Ahn, T.P. Ma, Ferroelectric field effect transistors for memory applications. Adv. Mater. 22(26–27), 2957–2961 (2010). doi:10.1002/adma.200904327
M. Tang, X. Xu, Z. Ye, Y. Sugiyama, H. Ishiwara, Impact of HfTaO buffer layer on data retention characteristics of ferroelectric-gate FET for nonvolatile memory applications. IEEE. Trans. Electron. Device 58(2), 370–375 (2011). doi:10.1109/TED.2010.2090883
L. Liao, H.J. Fan, B. Yan, Z. Zhang, L.L. Chen, B.S. Li, G.Z. Xing, Z.X. Shen, T. Wu, X.W. Sun, J. Wang, T. Yu, Ferroelectric transistors with nanowire channel: toward nonvolatile memory applications. ACS Nano 3(3), 700–706 (2009). doi:10.1021/nn800808s
J. Appenzeller, J. Knoch, M.T. Björk, H. Riel, H. Schmid, W. Riess, Toward nanowire electronics. IEEE. Trans. Electron. Device 55(11), 2827–2845 (2008). doi:10.1109/TED.2008.2008011
J. Xiang, W. Lu, Y. Hu, Y. Wu, H. Yan, C.M. Lieber, Ge/Si nanowire heterostructures as high-performance field-effect transistors. Nature 441(7092), 489–493 (2006). doi:10.1038/nature04796
Y. Cui, Z. Zhong, D. Wang, W.U. Wang, C.M. Lieber, High performance silicon nanowire field effect transistors. Nano Lett. 3(2), 149–152 (2003). doi:10.1021/nl025875l
J.Y. Son, S. Ryu, Y.C. Park, Y.T. Lim, Y.S. Shin, Y.H. Shin, H.M. Jang, A nonvolatile memory device made of a ferroelectric polymer gate nanodot and a single-walled carbon nanotube. ACS Nano 4(12), 7315–7320 (2010). doi:10.1021/nn1021296
Y. Zheng, G.X. Ni, C.T. Toh, C.Y. Tan, K. Yao, B. Özyilmaz, Graphene field-effect transistors with ferroelectric gating. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(16), 166602–166604 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.166602
T.W. Koo, D.S. Kim, J.H. Lee, Y.C. Jung, J.W. Lee, Y.S. Yu, S.W. Hwang, D. Whang, Axial p-n nanowire gated diodes as a direct probe of surface-dominated charge dynamics in semiconductor nanomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(47), 23552–23557 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp206639b
S. Cha, S.M. Kim, H. Kim, J. Ku, J.I. Sohn, Y.J. Park, B.G. Song, M.H. Jung, E.K. Lee, B.L. Choi, J.J. Park, Z.L. Wang, J.M. Kim, K. Kim, Porous PVDF as effective sonic wave driven nanogenerators. Nano Lett. 11(12), 5142–5147 (2011). doi:10.1021/nl202208n
O. Hayden, M.T. Björk, H. Schmid, H. Riel, U. Drechsler, S.F. Karg, E. Lörtscher, W. Riess, Fully depleted nanowire field-effect transistor in inversion mode. Small 3(2), 230–234 (2007). doi:10.1002/smll.200600325
W.W. Fang, N. Singh, K.L. Bera, H.S. Nguyen, S.C. Rustagi, G.Q. Lo, N. Balasubramanian, D.L. Kwong, Vertically stacked sige nanowire array channel cmos transistors. IEEE. Electron. Device Lett. 28(3), 211–213 (2007). doi:10.1109/LED.2007.891268
J.I. Sohn, S.S. Choi, S.M. Morris, J.S. Bendall, H.J. Coles, W.K. Hong, G. Jo, T. Lee, M.E. Welland, Novel nonvolatile memory with multibit storage based on a ZnO nanowire transistor. Nano Lett. 10(11), 4316–4320 (2010). doi:10.1021/nl1013713
S. Das, J. Appenzeller, FETRAM. An organic ferroelectric material based novel random access memory cell. Nano Lett. 11(9), 4003–4007 (2011). doi:10.1021/nl2023993
Y.T. Lee, P.J. Jeon, K.H. Lee, R. Ha, H.J. Choi, S. Im, Ferroelectric nonvolatile nanowire memory circuit using a single ZnO nanowire and copolymer top layer. Adv. Mater. 24(22), 3020–3025 (2012). doi:10.1002/adma.201201051
N.H. Van, J.H. Lee, J.I. Sohn, S.N. Cha, D. Whang, J.M. Kim, D.J. Kang, High performance Si nanowire field-effect-transistors based on a CMOS inverter with tunable threshold voltage. Nanoscale 6(10), 5479–5483 (2014). doi:10.1039/c3nr06690h
L.B. Luo, X.B. Yang, F.X. Liang, H. Xu, Y. Zhao, X. Xie, W.F. Zhang, S.T. Lee, Surface defects-induced p-type conduction of silicon nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 115(38), 18453–18458 (2011). doi:10.1021/jp205171j
K. Keem, D.Y. Jeong, S. Kim, M.S. Lee, I.S. Yeo, U.I. Chung, J.T. Moon, Fabrication and device characterization of omega-shaped-gate ZnO nanowire field-effect transistors. Nano Lett. 6(7), 1454–1458 (2006). doi:10.1021/nl060708x
H. Ishiwara, Current status of ferroelectric-gate Si transistors and challenge to ferroelectric-gate CNT transistors. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(1 Suppl.), S2–S6 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.cap.2008.02.013