Specific Recognition of Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro Using Near Infrared-Emitting Long-Persistence Luminescent Zn3Ga2Ge2O10:Cr3+ Nanoprobes
Corresponding Author: Hongwu Zhang
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 7 No. 2 (2015), Article Number: 138-145
Abstract
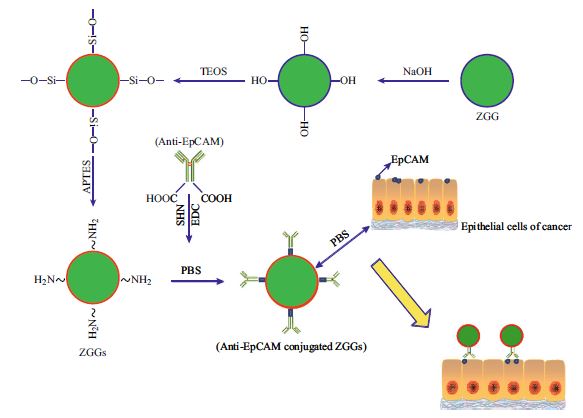
In this paper, near-infrared emitting long-persistence luminescent Zn3Ga2Ge2O10:Cr3+ (ZGG) nanoparticles with diameters of 30–100 nm and bright luminescence were prepared by a sol–gel synthesis method. After the surface amination, the nanoparticles were further bioconjugated with breast cancer-specific monoclonal antibody (anti-EpCAM) to form ZGG-EpCAM nanoprobes which can specifically target breast cancer cell lines (MCF7) in vitro. The results of in vitro images show that the luminescence signals from the cells treated with ZGG-EpCAM nanoprobes are stronger than those from cells treated with ZGG-unconjugated antibody, indicating that the prepared ZGG-EpCAM nanoprobes possessed excellent specific recognition capability. Furthermore, due to their long afterglow properties, the imaging could persist more than 1 h. Therefore, these nanoprobes could not only provide a high specificity detection method for cancer cells but also realize the long-time monitoring. Developed near-infrared emitting long-persistence luminescent nanoprobes will be expected to find new perspectives for cell therapy research and diagnosis applications.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- M. Bruchez, M. Moronne, P. Gin, Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281(5385), 2013–2016 (1998). doi:10.1126/science.281.5385.2013
- P.R. Banks, D.M. Paquette, Comparison of three common amine reactive fluorescent probes used for conjugation to biomolecules by capillary zone electrophoresis. Bioconjug. Chem. 6(4), 447–458 (1995). doi:10.1021/bc00034a015
- T. Kogure, S. Karasawa, T. Araki, K. Saito, M. Kinjo, A. Miyawaki, A fluorescent variant of a protein from the stonycoral Montipora facilitates dual-color single-laser fluorescence crosscorrelation spectroscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 24(5), 577–581 (2006). doi:10.1038/nbt1207
- W.C. Chan, S. Nie, Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281(5385), 2016–2018 (1998). doi:10.1126/science.281.5385.2016
- X. Michalet, F.F. Pinaud, L.A. Bentolila, J.M. Tsay, S. Doose, J.J. Li, G. Sundaresan, A.M. Wu, S.S. Gambhir, S. Weiss, Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307(5709), 538–544 (2005). doi:10.1126/science.1104274
- D. Maysinger, M. Behrendt, M. Lalancette-Hébert, J. Kriz, Real-time imaging of astrocyte response to quantum dots: in vivo screening model system for biocompatibility of nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 7(8), 2513–2520 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl071611t
- J.J. Storhoff, R. Elghanian, R.C. Mucic, C.A. Mirkin, R.L. Letsinger, One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120(9), 1959–1964 (1998). doi:10.1021/ja972332i
- T.A. Taton, C.A. Mirkin, R.L. Letsinger, Scanometric DNA array detection with nanoparticle probes. Science 289(5485), 1757–1760 (2000). doi:10.1126/science.289.5485.1757
- H. He, C. Xie, J. Ren, Nonbleaching fluorescence of gold nanoparticles and its applications in cancer cell imaging. Anal. Chem. 80(15), 5951–5957 (2008). doi:10.1021/ac8005796
- Y. Dai, P. Ma, Z. Cheng, Up-conversion cell imaging and pH-induced thermally controlled drug release from NaYF4: Yb3+/Er3+@ hydrogel core–shell hybrid microspheres. ACS Nano 6(4), 3327–3338 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn300303q
- V. Ntziachristos, Fluorescence molecular imaging. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 8, 1–33 (2006). doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095831
- J.V. Frangioni, In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 7(5), 626–634 (2003). doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.007
- B.W. Rice, M.D. Cable, M.B. Nelson, In vivo imaging of light-emitting probes. J. Biomed. Opt. 6(4), 432–440 (2001). doi:10.1117/1.1413210
- T. Matsuzawa, Y. Aoki, N. Takeuchi, Y. Murayama, A new long phosphorescent phosphor with high brightness, SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+. J. Electrochem. Soc. 143(8), 2670–2673 (1996). doi:10.1149/1.1837067
- T. Aitasalo, P. Dereń, J. Hölsä, H. Jungner, J.-C. Krupa, M. Lastusaari, J. Legendziewicz, J. Niittykoski, W. Stręk, Persistent luminescence phenomena in materials doped with rare earth ions. J. Solid State Chem. 171(1), 114–122 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0022-4596(02)00194-9
- Z.J. Li, H.W. Zhang, M. Sun, A facile and effective method to prepare long-persistent phosphorescent nanospheres and its potential application for in vivo imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 22(47), 24713–24720 (2012). doi:10.1039/c2jm35650c
- B.Y. Wu, H.F. Wang, J.T. Chen, X.P. Yan, Fluorescence resonance energy transfer inhibition assay for fetoprotein excreted during cancer cell growth using functionalized persistent luminescence nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(4), 686–688 (2010). doi:10.1021/ja108788p
- F. Liu, W.Z. Yan, Y.J. Chuang, Photostimulated near-infrared persistent luminescence as a new optical read-out from Cr3+-doped LiGa5O8. Sci. Rep. 3, 1554 (2013). doi:10.1038/srep01554
- A. Abdukayum, J.T. Chen, Q. Zhao, Functional near infrared-emitting Cr3+/Pr3+co-doped zinc gallogermanate persistent luminescent nanoparticles with superlong afterglow for in vivo targeted bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135(38), 14125–14133 (2013). doi:10.1021/ja404243v
- J. Shi, X. Sun, J. Li, Multifunctional near infrared-emitting long-persistence luminescent nanoprobes for drug delivery and targeted tumor imaging. Biomaterials 37, 260–270 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.033
- T. Maldiney, A. Bessière, J. Seguin, E. Teston, S.K. Sharma, B. Viana, A.J. Bos, P. Dorenbos, M. Bessodes, D. Gourier, The in vivo activation of persistent nanophors optical imaging of vascularization, tumors and grafted cells. Nat. Mater. 13(4), 418–426 (2014). doi:10.1038/nmat3908
- M.P. Melancon, M. Zhou, R. Zhang, Selective uptake and imaging of aptamer- and antibody-conjugated hollow nanospheres targeted to epidermal growth factor receptors overexpressed in head and neck cancer. ACS Nano 8, 4530–4538 (2014). doi:10.1021/nn406632u
- A. Farr, A. Nelson, J. Truex, S. Hosier, Epithelial heterogeneity in the murine thymus: a cell surface glycoprotein expressed by subcapsular and medullary epithelium. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39(5), 645–653 (1991). doi:10.1177/39.5.2016514
- A. Cimino, M. Halushka, P. Illei, X. Wu, S. Sukumar, P. Argani, Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is overexpressed in breast cancer metastases. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 123(3), 701–708 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0671-z
- J.M. Gostner, D. Fong, O.A. Wrulich, F. Lehne, M. Zitt, M. Hermann, S. Krobitsch, A. Martowicz, G. Gastl, G. Spizzo, Effects of EpCAM overexpression on human breast cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 11(1), 1471–2407 (2011). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-45
- Z.W. Pan, Y.Y. Lu, F. Liu, Sunlight-activated long-persistent luminescence in the near-infrared from Cr3+-doped zinc gallogermanates. Nat. Mater. 11(1), 58–63 (2012). doi:10.1038/nmat3173
References
M. Bruchez, M. Moronne, P. Gin, Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281(5385), 2013–2016 (1998). doi:10.1126/science.281.5385.2013
P.R. Banks, D.M. Paquette, Comparison of three common amine reactive fluorescent probes used for conjugation to biomolecules by capillary zone electrophoresis. Bioconjug. Chem. 6(4), 447–458 (1995). doi:10.1021/bc00034a015
T. Kogure, S. Karasawa, T. Araki, K. Saito, M. Kinjo, A. Miyawaki, A fluorescent variant of a protein from the stonycoral Montipora facilitates dual-color single-laser fluorescence crosscorrelation spectroscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 24(5), 577–581 (2006). doi:10.1038/nbt1207
W.C. Chan, S. Nie, Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281(5385), 2016–2018 (1998). doi:10.1126/science.281.5385.2016
X. Michalet, F.F. Pinaud, L.A. Bentolila, J.M. Tsay, S. Doose, J.J. Li, G. Sundaresan, A.M. Wu, S.S. Gambhir, S. Weiss, Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 307(5709), 538–544 (2005). doi:10.1126/science.1104274
D. Maysinger, M. Behrendt, M. Lalancette-Hébert, J. Kriz, Real-time imaging of astrocyte response to quantum dots: in vivo screening model system for biocompatibility of nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 7(8), 2513–2520 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl071611t
J.J. Storhoff, R. Elghanian, R.C. Mucic, C.A. Mirkin, R.L. Letsinger, One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120(9), 1959–1964 (1998). doi:10.1021/ja972332i
T.A. Taton, C.A. Mirkin, R.L. Letsinger, Scanometric DNA array detection with nanoparticle probes. Science 289(5485), 1757–1760 (2000). doi:10.1126/science.289.5485.1757
H. He, C. Xie, J. Ren, Nonbleaching fluorescence of gold nanoparticles and its applications in cancer cell imaging. Anal. Chem. 80(15), 5951–5957 (2008). doi:10.1021/ac8005796
Y. Dai, P. Ma, Z. Cheng, Up-conversion cell imaging and pH-induced thermally controlled drug release from NaYF4: Yb3+/Er3+@ hydrogel core–shell hybrid microspheres. ACS Nano 6(4), 3327–3338 (2012). doi:10.1021/nn300303q
V. Ntziachristos, Fluorescence molecular imaging. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 8, 1–33 (2006). doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.8.061505.095831
J.V. Frangioni, In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 7(5), 626–634 (2003). doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2003.08.007
B.W. Rice, M.D. Cable, M.B. Nelson, In vivo imaging of light-emitting probes. J. Biomed. Opt. 6(4), 432–440 (2001). doi:10.1117/1.1413210
T. Matsuzawa, Y. Aoki, N. Takeuchi, Y. Murayama, A new long phosphorescent phosphor with high brightness, SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+. J. Electrochem. Soc. 143(8), 2670–2673 (1996). doi:10.1149/1.1837067
T. Aitasalo, P. Dereń, J. Hölsä, H. Jungner, J.-C. Krupa, M. Lastusaari, J. Legendziewicz, J. Niittykoski, W. Stręk, Persistent luminescence phenomena in materials doped with rare earth ions. J. Solid State Chem. 171(1), 114–122 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0022-4596(02)00194-9
Z.J. Li, H.W. Zhang, M. Sun, A facile and effective method to prepare long-persistent phosphorescent nanospheres and its potential application for in vivo imaging. J. Mater. Chem. 22(47), 24713–24720 (2012). doi:10.1039/c2jm35650c
B.Y. Wu, H.F. Wang, J.T. Chen, X.P. Yan, Fluorescence resonance energy transfer inhibition assay for fetoprotein excreted during cancer cell growth using functionalized persistent luminescence nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(4), 686–688 (2010). doi:10.1021/ja108788p
F. Liu, W.Z. Yan, Y.J. Chuang, Photostimulated near-infrared persistent luminescence as a new optical read-out from Cr3+-doped LiGa5O8. Sci. Rep. 3, 1554 (2013). doi:10.1038/srep01554
A. Abdukayum, J.T. Chen, Q. Zhao, Functional near infrared-emitting Cr3+/Pr3+co-doped zinc gallogermanate persistent luminescent nanoparticles with superlong afterglow for in vivo targeted bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135(38), 14125–14133 (2013). doi:10.1021/ja404243v
J. Shi, X. Sun, J. Li, Multifunctional near infrared-emitting long-persistence luminescent nanoprobes for drug delivery and targeted tumor imaging. Biomaterials 37, 260–270 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.10.033
T. Maldiney, A. Bessière, J. Seguin, E. Teston, S.K. Sharma, B. Viana, A.J. Bos, P. Dorenbos, M. Bessodes, D. Gourier, The in vivo activation of persistent nanophors optical imaging of vascularization, tumors and grafted cells. Nat. Mater. 13(4), 418–426 (2014). doi:10.1038/nmat3908
M.P. Melancon, M. Zhou, R. Zhang, Selective uptake and imaging of aptamer- and antibody-conjugated hollow nanospheres targeted to epidermal growth factor receptors overexpressed in head and neck cancer. ACS Nano 8, 4530–4538 (2014). doi:10.1021/nn406632u
A. Farr, A. Nelson, J. Truex, S. Hosier, Epithelial heterogeneity in the murine thymus: a cell surface glycoprotein expressed by subcapsular and medullary epithelium. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39(5), 645–653 (1991). doi:10.1177/39.5.2016514
A. Cimino, M. Halushka, P. Illei, X. Wu, S. Sukumar, P. Argani, Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is overexpressed in breast cancer metastases. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 123(3), 701–708 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10549-009-0671-z
J.M. Gostner, D. Fong, O.A. Wrulich, F. Lehne, M. Zitt, M. Hermann, S. Krobitsch, A. Martowicz, G. Gastl, G. Spizzo, Effects of EpCAM overexpression on human breast cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 11(1), 1471–2407 (2011). doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-45
Z.W. Pan, Y.Y. Lu, F. Liu, Sunlight-activated long-persistent luminescence in the near-infrared from Cr3+-doped zinc gallogermanates. Nat. Mater. 11(1), 58–63 (2012). doi:10.1038/nmat3173