Detection of Adhesion Molecules on Inflamed Macrophages at Early-Stage Using SERS Probe Gold Nanorods
Corresponding Author: Dakrong Pissuwan
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 9 No. 1 (2017), Article Number: 8
Abstract
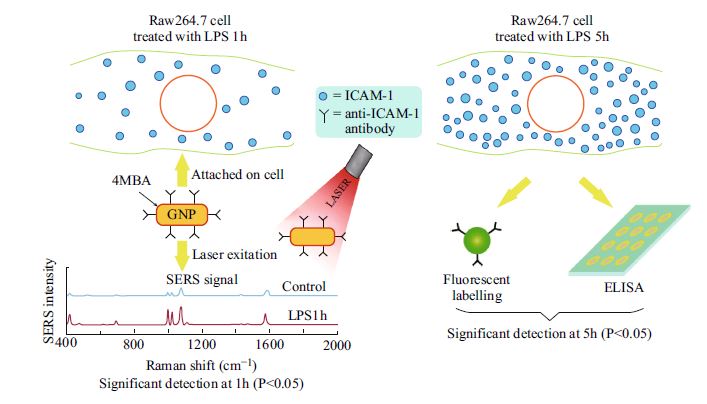
In recent years, it has been shown that inflammatory biomarkers can be used as an effective signal for disease diagnoses. The early detection of these signals provides useful information that could prevent the occurrence of severe diseases. Here, we employed surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) probe gold nanorods (GNRs) as a tool for the early detection of inflammatory molecules in inflamed cells. A murine macrophage cell line (Raw264.7) stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as a model in this study. The prepared SERS probe GNRs containing 4-mercaptobenzoic acid as a Raman reporter to generate SERS signals were used for detection of intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in macrophages after treatment with LPS for varying lengths of time. Our results show that SERS probe GNRs could detect significant differences in the expression of ICAM-1 molecules in LPS-treated macrophages compared to those in untreated macrophages after only 1 h of LPS treatment. In contrast, when using fluorescent labeling or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) to detect ICAM-1, significant differences between inflamed and un-inflamed macrophages were not seen until the cells had been treated with LPS for 5 h. These results indicate that our SERS probe GNRs provide a higher sensitivity for detecting biomarker molecules in inflamed macrophages than the conventional fluorescence and ELISA techniques, and could therefore be useful as a potential diagnostic tool for managing disease risk.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- P. Libby, P.M. Ridker, A. Maseri, Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105, 1135–1143 (2002). doi:10.1161/hc0902.104353
- A.K. Hubbard, C. Giardina, Regulation of ICAM-1 expression in mouse macrophages. Inflammation 24(2), 115–125 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1007029409521
- G.K. Hansson, P. Libby, The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6(7), 508–519 (2006). doi:10.1038/nri1882
- M. Goebeler, J. Roth, M. Kunz, C. Sorg, Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by murine macrophages is up-regulated during differentiation and inflammatory activation. Immunobiology 188(1–2), 159–171 (1993). doi:10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80495-X
- P.E. Rautou, A.S. Leroyer, B. Ramkhelawon, C. Devue, D. Duflaut et al., Microparticles from human atherosclerotic plaques promote endothelial ICAM-1-dependent monocyte adhesion and transendothelial migration. Circ. Res. 108, 335–343 (2011). doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.237420
- C.G. Kevil, H. Pruitt, T.J. Kavanagh, J. Wilkerson, F. Farin et al., Regulation of endothelial glutathione by ICAM-1: implications for inflammation. FASEB J. 18(11), 1321–1323 (2004). doi:10.1096/fj.03-1401fje
- B.A. Kaufmann, J.M. Sanders, C. Davis, A. Xie, P. Aldred, I.J. Sarembock, J.R. Lindner, Imaging molecular imaging of inflammation in atherosclerosis with targeted ultrasound detection of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Circulation 116(3), 276–284 (2007). doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.684738
- Z.A. Fayad, V. Fuster, Clinical imaging of the high-risk or vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque. Circ. Res. 89, 305–316 (2001). doi:10.1161/hh1601.095596
- J.T. Motz, M. Fitzmaurice, A. Miller, S.J. Gandhi, A.S. Haka et al., In vivo Raman spectral pathology of human atherosclerosis and vulnerable plaque. J. Biomed. Opt. 11(2), 021003 (2006). doi:10.1117/1.2190967
- M. Eisenblätter, J. Ehrchen, G. Varga, C. Sunderkötter, W. Heindel, J. Roth, C. Bremer, A. Wall, In vivo optical imaging of cellular inflammatory response in granuloma formation using fluorescence-labeled macrophages. J. Nucl. Med. 50(10), 1676–1682 (2009). doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.060707
- D. Pissuwan, S. Valenzuela, M.B. Cortie, Prospects for gold nanorod particles in diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 25(1), 93–112 (2008). doi:10.5661/bger-25-93
- K. Nose, D. Pissuwan, M. Goto, Y. Katayama, T. Niidome, Gold nanorods in an oil-base formulation for transdermal treatment of type 1 diabetes in mice. Nanoscale 4(12), 3776–3780 (2012). doi:10.1039/c2nr30651d
- X. Huang, S. Neretina, M.A. El-Sayed, Gold nanorods: from synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 21(48), 4880–4910 (2009). doi:10.1002/adma.200802789
- H. Liao, J.H. Hafner, Gold nanorod bioconjugates. Chem. Mater. 17(18), 4636–4641 (2005). doi:10.1021/cm050935k
- N. Harris, M.J. Ford, P. Mulvaney, M.B. Cortie, Tunable infrared absorption by metal nanoparticles: the case for gold rods and shells. Gold Bull. 41(1), 5–14 (2008). doi:10.1007/BF03215618
- P.K. Jain, K.S. Lee, I.H. El-Sayed, M.A. El-Sayed, Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7238–7248 (2006). doi:10.1021/jp057170o
- X. Huang, I.H. El-Sayed, W. Qian, M.A. El-Sayed, Cancer cells assemble and align gold nanorods conjugated to antibodies to produce highly enhanced, sharp, and polarized surface Raman spectra: a potential cancer diagnostic marker. Nano Lett. 7(6), 1591–1597 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl070472c
- H. Park, S. Lee, L. Chen, E.K. Lee, S.Y. Shin et al., SERS imaging of HER2-overexpressed MCF7 cells using antibody-conjugated gold nanorods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(34), 7444–7449 (2009). doi:10.1039/b904592a
- L. Jiang, J. Qian, F. Cai, S. He, Raman reporter-coated gold nanorods and their applications in multimodal optical imaging of cancer cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 400(9), 2793–2800 (2011). doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4894-6
- L. Wu, Z. Wang, S. Zong, Z. Huang, P. Zhang, Y. Cui, A SERS-based immunoassay with highly increased sensitivity using gold/silver core-shell nanorods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 38(1), 94–99 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.05.005
- M. Liu, Z. Wang, S. Zong, R. Zhang, J. Yang, Y. Cui, Intracellular surface-enhanced Raman scattering probe based on gold nanorods functionalized with mercaptohexadecanoic acid with reduced cytotoxicity. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 59(5), 381–387 (2012). doi:10.1002/bab.1035
- J. Yang, Z. Wang, S. Zong, C. Song, R. Zhang, Y. Cui, Distinguishing breast cancer cells using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 402(3), 1093–1100 (2012). doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5577-z
- R. McQueenie, R. Stevenson, R. Benson, N. MacRitchie, I. McInnes et al., Detection of inflammation in vivo by surface-enhanced Raman scattering provides higher sensitivity than conventional fluorescence imaging. Anal. Chem. 84(14), 5968–5975 (2012). doi:10.1021/ac3006445
- T. Takeshi, N. Keisuke, I. Takaaki, Y. Makoto, N. Tatsuji, Involvement of adhesion molecule in in vitro plaque-like formation of macrophages stimulated with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide. J. Periodontal Res. 45(4), 550–556 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01270.x
- K. Iiyama, L. Hajra, M. Iiyama, H. Li, M. DiChiara, B.D. Medoff, M.I. Cybulsky, Patterns of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in rabbit and mouse atherosclerotic lesions and at sites predisposed to lesion formation. Circ. Res. 85(2), 199–207 (1999). doi:10.1161/01.RES.85.2.199
- C. Wang, Y. Chen, T. Wang, Z. Ma, Z. Su, Monodispersed gold nanorod-embedded silica particles as novel Raman labels for biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(2), 355–361 (2008). doi:10.1002/adfm.200700503
- D.D. Li, J. Wang, G.C. Zheng, J.H. Liu, W.H. Xu, A highly active SERS sensing substrate: core–satellite assembly of gold nanorods/nanoplates. Nanotechnology 24(23), 235502 (2013). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/23/235502
- N. Pavillon, K. Bando, K. Fujita, N.I. Smith, Feature-based recognition of surface-enhanced Raman spectra for biological target. J. Biophotonics 6(8), 587–597 (2013). doi:10.1002/jbio.201200181
- D. Pissuwan, A.J. Hobro, N. Pavillon, N.I. Smith, Distribution of label free cationic polymer-coated gold nanorods in live macrophage cells reveals formation of groups of intracellular SERS signals of probe nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4(11), 5536–5541 (2014). doi:10.1039/c3ra45556d
- S. Zong, Z. Wang, J. Yang, C. Wang, S. Xu, Y. Cui, A SERS and fluorescence dual mode cancer cell targeting probe based on silica coated Au@Ag core–shell nanorods. Talanta 97(16), 368–375 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.04.047
- A. Michota, J. Bukowska, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid on silver and gold substrates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 34(1), 21–25 (2003). doi:10.1002/jrs.928
- C.E. Talley, L. Jusinski, C.W. Hollars, S.M. Lane, T. Huser, Intracellular pH sensors based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 76(23), 7064–7068 (2004). doi:10.1021/ac049093j
- J.-W. Cheng, Y. Lei, X.-J. Liu, J.-H. Jiang, G.-L. Shen, R.-Q. Yu, Immunoassay using surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on aggregation of reporter-labeled immunogold nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 392(1), 187–193 (2008). doi:10.1007/s00216-008-2237-z
- B.N. Khlebtsov, V.A. Khanadeev, M.Y. Tsvetkov, V.N. Bagratashvili, N.G. Khlebtsov, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on self-assembled PEGylated gold and gold–silver core–shell nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 117(44), 23162–23171 (2013). doi:10.1021/jp408359p
- T. Xuebin, W. Zhuyuan, Y. Jing, S. Chunyuan, Z. Ruohu, C. Yiping, Polyvinylpyrrolidone-(PVP-) coated silver aggregates for high performance surface-enhanced Raman scattering in living cells. Nanotechnology 20(44), 445102 (2009). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/44/445102
- W. Ji, L. Chen, X. Xue, Z. Guo, Z. Yu, B. Zhao, Y. Ozaki, Design of an anti-aggregated SERS sensing platform for metal ion detection based on bovine serum albumin-mediated metal nanoparticles. Chem. Comm. 49(66), 7334–7336 (2013). doi:10.1039/c3cc44517h
References
P. Libby, P.M. Ridker, A. Maseri, Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 105, 1135–1143 (2002). doi:10.1161/hc0902.104353
A.K. Hubbard, C. Giardina, Regulation of ICAM-1 expression in mouse macrophages. Inflammation 24(2), 115–125 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1007029409521
G.K. Hansson, P. Libby, The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6(7), 508–519 (2006). doi:10.1038/nri1882
M. Goebeler, J. Roth, M. Kunz, C. Sorg, Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 by murine macrophages is up-regulated during differentiation and inflammatory activation. Immunobiology 188(1–2), 159–171 (1993). doi:10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80495-X
P.E. Rautou, A.S. Leroyer, B. Ramkhelawon, C. Devue, D. Duflaut et al., Microparticles from human atherosclerotic plaques promote endothelial ICAM-1-dependent monocyte adhesion and transendothelial migration. Circ. Res. 108, 335–343 (2011). doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.237420
C.G. Kevil, H. Pruitt, T.J. Kavanagh, J. Wilkerson, F. Farin et al., Regulation of endothelial glutathione by ICAM-1: implications for inflammation. FASEB J. 18(11), 1321–1323 (2004). doi:10.1096/fj.03-1401fje
B.A. Kaufmann, J.M. Sanders, C. Davis, A. Xie, P. Aldred, I.J. Sarembock, J.R. Lindner, Imaging molecular imaging of inflammation in atherosclerosis with targeted ultrasound detection of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Circulation 116(3), 276–284 (2007). doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.684738
Z.A. Fayad, V. Fuster, Clinical imaging of the high-risk or vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque. Circ. Res. 89, 305–316 (2001). doi:10.1161/hh1601.095596
J.T. Motz, M. Fitzmaurice, A. Miller, S.J. Gandhi, A.S. Haka et al., In vivo Raman spectral pathology of human atherosclerosis and vulnerable plaque. J. Biomed. Opt. 11(2), 021003 (2006). doi:10.1117/1.2190967
M. Eisenblätter, J. Ehrchen, G. Varga, C. Sunderkötter, W. Heindel, J. Roth, C. Bremer, A. Wall, In vivo optical imaging of cellular inflammatory response in granuloma formation using fluorescence-labeled macrophages. J. Nucl. Med. 50(10), 1676–1682 (2009). doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.060707
D. Pissuwan, S. Valenzuela, M.B. Cortie, Prospects for gold nanorod particles in diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 25(1), 93–112 (2008). doi:10.5661/bger-25-93
K. Nose, D. Pissuwan, M. Goto, Y. Katayama, T. Niidome, Gold nanorods in an oil-base formulation for transdermal treatment of type 1 diabetes in mice. Nanoscale 4(12), 3776–3780 (2012). doi:10.1039/c2nr30651d
X. Huang, S. Neretina, M.A. El-Sayed, Gold nanorods: from synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 21(48), 4880–4910 (2009). doi:10.1002/adma.200802789
H. Liao, J.H. Hafner, Gold nanorod bioconjugates. Chem. Mater. 17(18), 4636–4641 (2005). doi:10.1021/cm050935k
N. Harris, M.J. Ford, P. Mulvaney, M.B. Cortie, Tunable infrared absorption by metal nanoparticles: the case for gold rods and shells. Gold Bull. 41(1), 5–14 (2008). doi:10.1007/BF03215618
P.K. Jain, K.S. Lee, I.H. El-Sayed, M.A. El-Sayed, Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7238–7248 (2006). doi:10.1021/jp057170o
X. Huang, I.H. El-Sayed, W. Qian, M.A. El-Sayed, Cancer cells assemble and align gold nanorods conjugated to antibodies to produce highly enhanced, sharp, and polarized surface Raman spectra: a potential cancer diagnostic marker. Nano Lett. 7(6), 1591–1597 (2007). doi:10.1021/nl070472c
H. Park, S. Lee, L. Chen, E.K. Lee, S.Y. Shin et al., SERS imaging of HER2-overexpressed MCF7 cells using antibody-conjugated gold nanorods. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(34), 7444–7449 (2009). doi:10.1039/b904592a
L. Jiang, J. Qian, F. Cai, S. He, Raman reporter-coated gold nanorods and their applications in multimodal optical imaging of cancer cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 400(9), 2793–2800 (2011). doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4894-6
L. Wu, Z. Wang, S. Zong, Z. Huang, P. Zhang, Y. Cui, A SERS-based immunoassay with highly increased sensitivity using gold/silver core-shell nanorods. Biosens. Bioelectron. 38(1), 94–99 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.05.005
M. Liu, Z. Wang, S. Zong, R. Zhang, J. Yang, Y. Cui, Intracellular surface-enhanced Raman scattering probe based on gold nanorods functionalized with mercaptohexadecanoic acid with reduced cytotoxicity. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 59(5), 381–387 (2012). doi:10.1002/bab.1035
J. Yang, Z. Wang, S. Zong, C. Song, R. Zhang, Y. Cui, Distinguishing breast cancer cells using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 402(3), 1093–1100 (2012). doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5577-z
R. McQueenie, R. Stevenson, R. Benson, N. MacRitchie, I. McInnes et al., Detection of inflammation in vivo by surface-enhanced Raman scattering provides higher sensitivity than conventional fluorescence imaging. Anal. Chem. 84(14), 5968–5975 (2012). doi:10.1021/ac3006445
T. Takeshi, N. Keisuke, I. Takaaki, Y. Makoto, N. Tatsuji, Involvement of adhesion molecule in in vitro plaque-like formation of macrophages stimulated with Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans lipopolysaccharide. J. Periodontal Res. 45(4), 550–556 (2010). doi:10.1111/j.1600-0765.2010.01270.x
K. Iiyama, L. Hajra, M. Iiyama, H. Li, M. DiChiara, B.D. Medoff, M.I. Cybulsky, Patterns of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in rabbit and mouse atherosclerotic lesions and at sites predisposed to lesion formation. Circ. Res. 85(2), 199–207 (1999). doi:10.1161/01.RES.85.2.199
C. Wang, Y. Chen, T. Wang, Z. Ma, Z. Su, Monodispersed gold nanorod-embedded silica particles as novel Raman labels for biosensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 18(2), 355–361 (2008). doi:10.1002/adfm.200700503
D.D. Li, J. Wang, G.C. Zheng, J.H. Liu, W.H. Xu, A highly active SERS sensing substrate: core–satellite assembly of gold nanorods/nanoplates. Nanotechnology 24(23), 235502 (2013). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/24/23/235502
N. Pavillon, K. Bando, K. Fujita, N.I. Smith, Feature-based recognition of surface-enhanced Raman spectra for biological target. J. Biophotonics 6(8), 587–597 (2013). doi:10.1002/jbio.201200181
D. Pissuwan, A.J. Hobro, N. Pavillon, N.I. Smith, Distribution of label free cationic polymer-coated gold nanorods in live macrophage cells reveals formation of groups of intracellular SERS signals of probe nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 4(11), 5536–5541 (2014). doi:10.1039/c3ra45556d
S. Zong, Z. Wang, J. Yang, C. Wang, S. Xu, Y. Cui, A SERS and fluorescence dual mode cancer cell targeting probe based on silica coated Au@Ag core–shell nanorods. Talanta 97(16), 368–375 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.04.047
A. Michota, J. Bukowska, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid on silver and gold substrates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 34(1), 21–25 (2003). doi:10.1002/jrs.928
C.E. Talley, L. Jusinski, C.W. Hollars, S.M. Lane, T. Huser, Intracellular pH sensors based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 76(23), 7064–7068 (2004). doi:10.1021/ac049093j
J.-W. Cheng, Y. Lei, X.-J. Liu, J.-H. Jiang, G.-L. Shen, R.-Q. Yu, Immunoassay using surface-enhanced Raman scattering based on aggregation of reporter-labeled immunogold nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 392(1), 187–193 (2008). doi:10.1007/s00216-008-2237-z
B.N. Khlebtsov, V.A. Khanadeev, M.Y. Tsvetkov, V.N. Bagratashvili, N.G. Khlebtsov, Surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates based on self-assembled PEGylated gold and gold–silver core–shell nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 117(44), 23162–23171 (2013). doi:10.1021/jp408359p
T. Xuebin, W. Zhuyuan, Y. Jing, S. Chunyuan, Z. Ruohu, C. Yiping, Polyvinylpyrrolidone-(PVP-) coated silver aggregates for high performance surface-enhanced Raman scattering in living cells. Nanotechnology 20(44), 445102 (2009). doi:10.1088/0957-4484/20/44/445102
W. Ji, L. Chen, X. Xue, Z. Guo, Z. Yu, B. Zhao, Y. Ozaki, Design of an anti-aggregated SERS sensing platform for metal ion detection based on bovine serum albumin-mediated metal nanoparticles. Chem. Comm. 49(66), 7334–7336 (2013). doi:10.1039/c3cc44517h