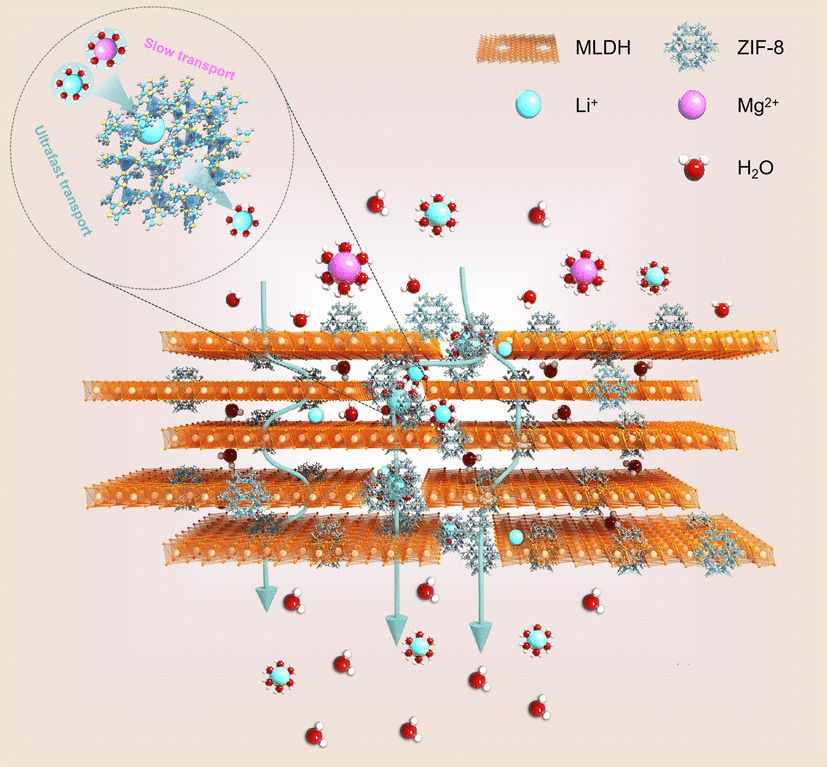
Engineer Nanoscale Defects into Selective Channels: MOF-Enhanced Li+ Separation by Porous Layered Double Hydroxide Membrane
Corresponding Author: Jiayin Yuan
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 15 (2023), Article Number: 147
Abstract
Two-dimensional (2D) membrane-based ion separation technology has been increasingly explored to address the problem of lithium resource shortage, yet it remains a sound challenge to design 2D membranes of high selectivity and permeability for ion separation applications. Zeolitic imidazolate framework functionalized modified layered double hydroxide (ZIF-8@MLDH) composite membranes with high lithium-ion (Li+) permeability and excellent operational stability were obtained in this work by in situ depositing functional ZIF-8 nanoparticles into the nanopores acting as framework defects in MLDH membranes. The defect-rich framework amplified the permeability of Li+, and the site-selective growth of ZIF-8 in the framework defects bettered its selectivity. Specifically speaking, the ZIF-8@MLDH membranes featured a high permeation rate of Li+ up to 1.73 mol m−2 h−1 and a desirable selectivity of Li+/Mg2+ up to 31.9. Simulations supported that the simultaneously enhanced selectivity and permeability of Li+ are attributed to changes in the type of mass transfer channels and the difference in the dehydration capacity of hydrated metal cations when they pass through nanochannels of ZIF-8. This study will inspire the ongoing research of high-performance 2D membranes through the engineering of defects.
Highlights:
1 The zeolitic imidazolate framework functionalized modified layered double hydroxide (ZIF-8@MLDH) composite membranes with superior structural stability and Li+ permeability are prepared by selectively growing ZIF-8 nanoparticles in the framework defects of the MLDH membrane.
2 The tailor-made ZIF-8@MLDH membrane has a large Li+ permeability of up to 1.73 mol m-2 h-1 and a high Li+/Mg2+ selectivity of 31.9, which exceed most of the current 2D lamellar membranes.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- P. Greim, A.A. Solomon, C. Breyer, Assessment of lithium criticality in the global energy transition and addressing policy gaps in transportation. Nat. Commun. 11, 4570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18402-y
- S. Yang, F. Zhang, H. Ding, P. He, H. Zhou, Lithium metal extraction from seawater. Joule 2, 1648 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.07.006
- G. Wu, M. Huang, Organolithium reagents in pharmaceutical asymmetric processes. Chem. Rev. 106, 2596 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040694k
- Y. Guo, Y. Ying, Y. Mao, X. Peng, B. Chen, Polystyrene sulfonate threaded through a metal - organic framework membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 128, 15344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201607329
- J. Song, X.M. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Yin, B. Zhao et al., Hydrophilic nanoporous ion-exchange membranes as a stabilizing barrier for liquid-liquid membrane extraction of lithium ions. J. Membr. Sci. 471, 372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.08.010
- A. Razmjou, M. Asadnia, E. Hosseini, A.H. Korayem, V. Chen, Design principles of ion selective nanostructured membranes for the extraction of lithium ions. Nat. Commun. 10, 5793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13648-7
- Y.Q. Zhang, F. Yang, H.G. Sun, Y.P. Bai, S.W. Li et al., Building a highly stable ultrathin nanoporous layer assisted by glucose for desalination. Engineering 16, 247 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.06.033
- W.G. Wang, G.H. Hong, Y.Q. Zhang, X.B. Yang, N.M. Hu et al., Designing an energy-efficient multi-stage selective electrodialysis process based on high-performance materials for lithium extraction. J. Membr. Sci. 675, 121534 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2023.121534
- Q. Wen, D. Yan, F. Liu, M. Wang, Y. Ling et al., Highly selective ionic transport through subnanometer pores in polymer films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 5796 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201601689
- Y. Li, Y. Zhao, H. Wang, M. Wang, The application of nanofiltration membrane for recovering lithium from salt lake brine. Desalination 468, 114081 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114081
- Z. Lu, Y. Wu, L. Ding, Y. Wei, H. Wang, A lamellar MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/PSS composite membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 133, 22439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202108801
- L. Ding, L. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wu, Z. Lu et al., Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater. Nat. Sustain. 3, 296 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-0474-0
- J. Zhu, L. Wang, J. Wang, F. Wang, M. Tian et al., Precisely tunable ion sieving with an al13-ti3c2tx lamellar membrane by controlling interlayer spacing. ACS Nano 14, 15306 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c05649
- C. Tan, X. Cao, X. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang et al., Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 117, 6225 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00558
- M.C. Zhang, K. Guan, Y. Ji, G. Liu, W. Jin et al., Controllable ion transport by surface-charged graphene oxide membrane. Nat. Commun. 10, 1253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09286-8
- S.P. Surwade, S.N. Smirnov, I.V. Vlassiouk, R.R. Unocic, G.M. Veith et al., Water desalination using nanoporous single-layer graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 459 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.37
- Y. Han, Z. Xu, C. Gao, Ultrathin graphene nanofiltration membrane for water purification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 3693 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201202601
- J. Lu, H. Zhang, J. Hou, X. Li, X. Hu et al., Efficient metal ion sieving in rectifying subnanochannels enabled by metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 19, 767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0634-7
- C.Y. Zhang, Y.X. Mu, W. Zhang, S. Zhao, Y.X. Wang, PVC-based hybrid membranes containing metal-organic frameworks for Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 596, 117724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117724
- R.M. Xu, Y. Kang, W.M. Zhang, X.W. Zhang, B.C. Pan, Oriented UiO-67 metal-organic framework membrane with fast and selective lithium-ion transport. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202115443 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202115443
- Q. Bian, M. Zhang, Y. Liu, L. Liu, Y. Li et al., Layered double hydroxide-assisted fabrication of prussian blue membranes for precise molecular sieving. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202113662 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202113662
- E.H. Ang, S. Velioğlu, J.W. Chew, Tunable affinity separation enables ultrafast solvent permeation through layered double hydroxide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 591, 117318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117318
- H.F. Liang, L.S. Li, F. Meng, L.N. Dang, J.Q. Zhuo et al., Porous two-dimensional nanosheets converted from layered double hydroxides and their applications in electrocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Mater. 27, 5702 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b02177
- X.Z. Xu, J.J. Wang, A. Zhou, S.Y. Dong, K.Q. Shi et al., High-efficiency CO2 separation using hybrid LDH-polymer membranes. Nat. Commun. 12, 3069 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23121-z
- N. Iyi, T. Matsumoto, Y. Kaneko, K. Kitamura, A novel synthetic route to layered double hydroxides using hexamethylenetetramine. Chem. Lett. 33, 1122 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.2004.1122
- L. Li, R. Ma, Y. Ebina, N. Iyi, T. Sasaki, Positively charged nanosheets derived via total delamination of layered double hydroxides. Chem. Mater. 17, 4386 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0510460
- S. Furukawa, J. Reboul, S. Diring, K. Sumida, S. Kitagawa, Structuring of metal-organic frameworks at the mesoscopic/macroscopic scale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 5700 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00106k
- K. Shen, L. Zhang, X. Chen, L. Liu, D. Zhang et al., Ordered macro-microporous metal-organic framework single crystals. Science 359, 206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao3403
- X.C. Huang, Y.Y. Lin, J.P. Zhang, X.P. Chen, Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal-organic frameworks: zinc(ii) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 1557 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200503778
- C.E. Ren, K.B. Hatzell, M. Alhabeb, Z. Ling, K.A. Mahmoud et al., Charge- and size-selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 4026 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01895
- S. Liang, S. Wang, L. Chen, H. Fang, Controlling interlayer spacings of graphene oxide membranes with cationic for precise sieving of mono-/multi-valent ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 241, 116738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116738
- F.M. Sheng, B. Wu, X.Y. Li, T.T. Xu, M.A. Shehzad et al., Efficient Ion sieving in covalent organic framework membranes with sub-2-nanometer channels. Adv. Mater. 33, 2104404 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202104404
- M.C. Zhang, P.X. Zhao, P.S. Li, Y.F. Ji, G.P. Liu et al., Designing biomimic two-dimensional ionic transport channels for efficient ion sieving. ACS Nano 15, 5209 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c10451
- Y.H. Xi, Z. Liu, J. Ji, Y. Wang, Y. Faraj et al., Graphene-based membranes with uniform 2D nanochannels for precise sieving of mono-/multi-valent metal ions. J. Membr. Sci. 550, 208 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.12.057
- J.J. Deng, Z. Lu, L. Ding, Z.K. Li, Y.Y. Wei et al., Fast electrophoretic preparation of large-area two-dimensional titanium carbide membranes for ion sieving. Chem. Eng. J. 408, 127806 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127806
References
P. Greim, A.A. Solomon, C. Breyer, Assessment of lithium criticality in the global energy transition and addressing policy gaps in transportation. Nat. Commun. 11, 4570 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18402-y
S. Yang, F. Zhang, H. Ding, P. He, H. Zhou, Lithium metal extraction from seawater. Joule 2, 1648 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2018.07.006
G. Wu, M. Huang, Organolithium reagents in pharmaceutical asymmetric processes. Chem. Rev. 106, 2596 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr040694k
Y. Guo, Y. Ying, Y. Mao, X. Peng, B. Chen, Polystyrene sulfonate threaded through a metal - organic framework membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 128, 15344 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201607329
J. Song, X.M. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Yin, B. Zhao et al., Hydrophilic nanoporous ion-exchange membranes as a stabilizing barrier for liquid-liquid membrane extraction of lithium ions. J. Membr. Sci. 471, 372 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.08.010
A. Razmjou, M. Asadnia, E. Hosseini, A.H. Korayem, V. Chen, Design principles of ion selective nanostructured membranes for the extraction of lithium ions. Nat. Commun. 10, 5793 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13648-7
Y.Q. Zhang, F. Yang, H.G. Sun, Y.P. Bai, S.W. Li et al., Building a highly stable ultrathin nanoporous layer assisted by glucose for desalination. Engineering 16, 247 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2020.06.033
W.G. Wang, G.H. Hong, Y.Q. Zhang, X.B. Yang, N.M. Hu et al., Designing an energy-efficient multi-stage selective electrodialysis process based on high-performance materials for lithium extraction. J. Membr. Sci. 675, 121534 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2023.121534
Q. Wen, D. Yan, F. Liu, M. Wang, Y. Ling et al., Highly selective ionic transport through subnanometer pores in polymer films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 26, 5796 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201601689
Y. Li, Y. Zhao, H. Wang, M. Wang, The application of nanofiltration membrane for recovering lithium from salt lake brine. Desalination 468, 114081 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114081
Z. Lu, Y. Wu, L. Ding, Y. Wei, H. Wang, A lamellar MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/PSS composite membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 133, 22439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202108801
L. Ding, L. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Wu, Z. Lu et al., Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater. Nat. Sustain. 3, 296 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-0474-0
J. Zhu, L. Wang, J. Wang, F. Wang, M. Tian et al., Precisely tunable ion sieving with an al13-ti3c2tx lamellar membrane by controlling interlayer spacing. ACS Nano 14, 15306 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c05649
C. Tan, X. Cao, X. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang et al., Recent advances in ultrathin two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chem. Rev. 117, 6225 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00558
M.C. Zhang, K. Guan, Y. Ji, G. Liu, W. Jin et al., Controllable ion transport by surface-charged graphene oxide membrane. Nat. Commun. 10, 1253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09286-8
S.P. Surwade, S.N. Smirnov, I.V. Vlassiouk, R.R. Unocic, G.M. Veith et al., Water desalination using nanoporous single-layer graphene. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 459 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2015.37
Y. Han, Z. Xu, C. Gao, Ultrathin graphene nanofiltration membrane for water purification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 3693 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201202601
J. Lu, H. Zhang, J. Hou, X. Li, X. Hu et al., Efficient metal ion sieving in rectifying subnanochannels enabled by metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 19, 767 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0634-7
C.Y. Zhang, Y.X. Mu, W. Zhang, S. Zhao, Y.X. Wang, PVC-based hybrid membranes containing metal-organic frameworks for Li+/Mg2+ separation. J. Membr. Sci. 596, 117724 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117724
R.M. Xu, Y. Kang, W.M. Zhang, X.W. Zhang, B.C. Pan, Oriented UiO-67 metal-organic framework membrane with fast and selective lithium-ion transport. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202115443 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202115443
Q. Bian, M. Zhang, Y. Liu, L. Liu, Y. Li et al., Layered double hydroxide-assisted fabrication of prussian blue membranes for precise molecular sieving. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 61, e202113662 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202113662
E.H. Ang, S. Velioğlu, J.W. Chew, Tunable affinity separation enables ultrafast solvent permeation through layered double hydroxide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 591, 117318 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117318
H.F. Liang, L.S. Li, F. Meng, L.N. Dang, J.Q. Zhuo et al., Porous two-dimensional nanosheets converted from layered double hydroxides and their applications in electrocatalytic water splitting. Chem. Mater. 27, 5702 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b02177
X.Z. Xu, J.J. Wang, A. Zhou, S.Y. Dong, K.Q. Shi et al., High-efficiency CO2 separation using hybrid LDH-polymer membranes. Nat. Commun. 12, 3069 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23121-z
N. Iyi, T. Matsumoto, Y. Kaneko, K. Kitamura, A novel synthetic route to layered double hydroxides using hexamethylenetetramine. Chem. Lett. 33, 1122 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.2004.1122
L. Li, R. Ma, Y. Ebina, N. Iyi, T. Sasaki, Positively charged nanosheets derived via total delamination of layered double hydroxides. Chem. Mater. 17, 4386 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0510460
S. Furukawa, J. Reboul, S. Diring, K. Sumida, S. Kitagawa, Structuring of metal-organic frameworks at the mesoscopic/macroscopic scale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 5700 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00106k
K. Shen, L. Zhang, X. Chen, L. Liu, D. Zhang et al., Ordered macro-microporous metal-organic framework single crystals. Science 359, 206 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao3403
X.C. Huang, Y.Y. Lin, J.P. Zhang, X.P. Chen, Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal-organic frameworks: zinc(ii) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 1557 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200503778
C.E. Ren, K.B. Hatzell, M. Alhabeb, Z. Ling, K.A. Mahmoud et al., Charge- and size-selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 4026 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01895
S. Liang, S. Wang, L. Chen, H. Fang, Controlling interlayer spacings of graphene oxide membranes with cationic for precise sieving of mono-/multi-valent ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 241, 116738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116738
F.M. Sheng, B. Wu, X.Y. Li, T.T. Xu, M.A. Shehzad et al., Efficient Ion sieving in covalent organic framework membranes with sub-2-nanometer channels. Adv. Mater. 33, 2104404 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202104404
M.C. Zhang, P.X. Zhao, P.S. Li, Y.F. Ji, G.P. Liu et al., Designing biomimic two-dimensional ionic transport channels for efficient ion sieving. ACS Nano 15, 5209 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c10451
Y.H. Xi, Z. Liu, J. Ji, Y. Wang, Y. Faraj et al., Graphene-based membranes with uniform 2D nanochannels for precise sieving of mono-/multi-valent metal ions. J. Membr. Sci. 550, 208 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.12.057
J.J. Deng, Z. Lu, L. Ding, Z.K. Li, Y.Y. Wei et al., Fast electrophoretic preparation of large-area two-dimensional titanium carbide membranes for ion sieving. Chem. Eng. J. 408, 127806 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127806