Reducing SU-8 hygroscopic swelling by ultrasonic treatment
Corresponding Author: Liqun Du
Nano-Micro Letters,
Vol. 2 No. 3 (2010), Article Number: 197-203
Abstract
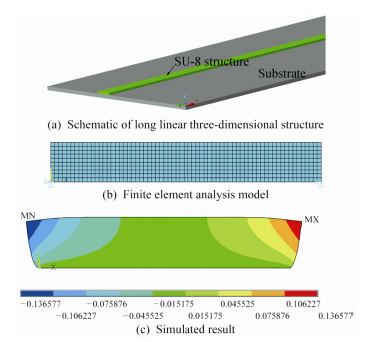
The volume expansion of SU-8 resist brings serious dimensional errors to electroformed structures. Two approaches have been proposed to reduce resist distortions during electroforming: electroforming at room temperature and adding auxiliary features for mask patterns. However, the former method induces higher internal stresses in the electroformed metal layers. And the latter method makes it difficult to predict the expansion behaviors of the resists. In the paper, the thermal expansion of the SU-8 mould is calculated by ANSYS firstly, and the lower thermal expansion value indicates that hygroscopic swelling plays a leading role in SU-8 mould distortions. An original technique is presented to reduce SU-8 hygroscopic swelling by ultrasonic treatment. The dimensional errors of the electroformed structure fabricated on the ultrasonic treatment mould are 50% lower than the one without ultrasonic treatment. Simulation of hygroscopic swelling is conducted by finite element analysis, and the results indicate that the hygroscopic strain ε of SU-8 after electroforming is declined from 6.8% to 3.1% because of ultrasonic. The measurements show that ultrasonic treatment increased the water contact angle of cured SU-8 from 70.8° to 74.9°. Based on these results, the mechanism of ultrasonic effect on hygroscopic swelling is proposed from the view of ultrasonic vibration decreasing the number of hydroxyl groups in SU-8. The research presents a novel method to improve the precisions of electroformed structures. It has no influence on the internal stresses of final structures and does not increase the complexities of mask layouts.
Keywords
Download Citation
Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)BibTeX
- C. Ho and W. Hsu, J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 356 (2004). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/14/3/007
- M. Agarwal, R. A.Gunasekaran and P. Coane, et al, J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 130–135 (2005). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/1/020
- L. Du, S. Zhu and C. Liu, Piezoelect. Acoustooptic. 30, 621 (2008).
- L. Du, S. Zhu and L. Yu, Opt. Precis. Eng. 16, 500 (2008).
- S. K Grif, J. A. W. Crowell, B. L. Kistler, et al, J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 1548 (2004). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/14/11/017
- A. Ruzzu and B. Matthis, Microsyst. Technol. 8, 116 (2002). doi:10.1007/s00542-001-0138-6
- A. Du, J. Long and H. Pei, et al, Electroplat. Finish. 27, 15 (2008).
- G. Aigeldinger, J. T. Ceremugaj and B. E. Mills, et al,.: ‘Final-Part Metrology for LIGA Springs, Build 1’, Sandia Report, Sandia National Laboratories, 2004
- C. Solf, A. Janssen and J. Mohr, et al, Microsyst. Technol. 10, 706 (2004). doi:10.1007/s00542-004-0406-3
- G. Aigeldinger, J. T. Ceremuga and K. D. Krenz, Proceedings ASPE 2004 annual meeting (2004).
- N. Chronis and L. P. Leel, 17th IEEE International Conference on Micro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), pp. 17–20 (2004).
- S. Zhang, Y. Kong and Y. Ding, et al, Acta Phys. Chem. Sin. 20, 360 (2004).
- M. J. Adamson, J. Mater. Sci. 15, 1736 (1980). doi:10.1007/BF00550593
- S. Luo, J. Leisen and C. P. Wong, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 85, 1 (2002). doi:10.1002/app.10473
- S. Popineau, C. Rondeau-Mouro and C. Sulpoce-Gaillet, et al, Polymer, 46, 10733 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.09.008
- R. Feng and J. Farris, J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 80 (2003). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/13/1/312
- Y. Hiral, Y. Inamoto and K. Sugano, et al, J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 199 (2007). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/17/2/003
- Z. Zhou, Q. Huang and W. Li, et al, IEEE Conf. Proc. Sensor, 325 (2007).
- C. L. Soles, F. T. Chang and D. W. Gidley, et al, J. Polym. Sci. 38, 776 (2000).
- J. Kost, L. Leong and R. Langer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7663 (1989). doi:10.1073/pnas.86.20.7663
References
C. Ho and W. Hsu, J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 356 (2004). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/14/3/007
M. Agarwal, R. A.Gunasekaran and P. Coane, et al, J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 130–135 (2005). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/1/020
L. Du, S. Zhu and C. Liu, Piezoelect. Acoustooptic. 30, 621 (2008).
L. Du, S. Zhu and L. Yu, Opt. Precis. Eng. 16, 500 (2008).
S. K Grif, J. A. W. Crowell, B. L. Kistler, et al, J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 1548 (2004). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/14/11/017
A. Ruzzu and B. Matthis, Microsyst. Technol. 8, 116 (2002). doi:10.1007/s00542-001-0138-6
A. Du, J. Long and H. Pei, et al, Electroplat. Finish. 27, 15 (2008).
G. Aigeldinger, J. T. Ceremugaj and B. E. Mills, et al,.: ‘Final-Part Metrology for LIGA Springs, Build 1’, Sandia Report, Sandia National Laboratories, 2004
C. Solf, A. Janssen and J. Mohr, et al, Microsyst. Technol. 10, 706 (2004). doi:10.1007/s00542-004-0406-3
G. Aigeldinger, J. T. Ceremuga and K. D. Krenz, Proceedings ASPE 2004 annual meeting (2004).
N. Chronis and L. P. Leel, 17th IEEE International Conference on Micro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), pp. 17–20 (2004).
S. Zhang, Y. Kong and Y. Ding, et al, Acta Phys. Chem. Sin. 20, 360 (2004).
M. J. Adamson, J. Mater. Sci. 15, 1736 (1980). doi:10.1007/BF00550593
S. Luo, J. Leisen and C. P. Wong, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 85, 1 (2002). doi:10.1002/app.10473
S. Popineau, C. Rondeau-Mouro and C. Sulpoce-Gaillet, et al, Polymer, 46, 10733 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2005.09.008
R. Feng and J. Farris, J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 80 (2003). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/13/1/312
Y. Hiral, Y. Inamoto and K. Sugano, et al, J. Micromech. Microeng. 17, 199 (2007). doi:10.1088/0960-1317/17/2/003
Z. Zhou, Q. Huang and W. Li, et al, IEEE Conf. Proc. Sensor, 325 (2007).
C. L. Soles, F. T. Chang and D. W. Gidley, et al, J. Polym. Sci. 38, 776 (2000).
J. Kost, L. Leong and R. Langer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 7663 (1989). doi:10.1073/pnas.86.20.7663